Stable silencing of ROR1 regulates cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy in a lung adenocarcinoma cell line
- PMID: 32509086
- PMCID: PMC7270672
Stable silencing of ROR1 regulates cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy in a lung adenocarcinoma cell line
Abstract
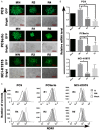
Lung cancer has the highest mortality and recurrence rate among cancers in the world. Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) has been widely recognized for its role in promoting the growth and metastasis of lung cancer, but its comprehensive role and molecular mechanisms in regulating cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy remain unclear. In this study, a series of ROR1-stably silenced monoclonal clones from lung adenocarcinoma cell lines PC9, PC9erlo, and NCI-H1975 were successfully selected and confirmed by qRT-PCR, western blot, and flow cytometry, and used as cell models in the following assays. Our study clearly shows that blocking ROR1 significantly downregulates cell cycle-inducing molecules such as CDK4 and Cyclin E1, and anti-apoptotic molecules such as Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, while it markedly upregulates pro-apoptotic molecules such as Bak, Caspase-3, and Caspase-7, which extends our previous observation on the molecular mechanism of ROR1-mediated tumor growth in lung adenocarcinoma. Our data also show that silencing ROR1 promotes autophagy since the key molecules involved in autophagy including ATG7, ATG12, BNIP3L, LC3A, LC3B, and NBS1 were up-regulated. We further screened key phosphokinase signaling pathways downstream of ROR1 in lung adenocarcinoma by a human phospho-kinase array. Our data indicate that blocking ROR1 could deactivate Akt, then activate GSK-3α/β by de-phosphorylation, and finally deactivate mTOR. In this way blocking ROR1 could effectively regulate the cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy in lung cancer.
Keywords: ROR1; apoptosis; autophagy; cell cycle; lung adenocarcinoma.
IJCEP Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
