Expression and clinical significance of Gal-3 and NFκB pathway-related factors in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- PMID: 32509095
- PMCID: PMC7270682
Expression and clinical significance of Gal-3 and NFκB pathway-related factors in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To explore the expression and clinical significance of Gal-3 and NFκB pathway related factors in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells.
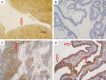
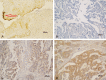
Methods: 99 histologic specimens of epithelial ovarian cancer and 20 normal ovarian histologic specimens were collected, and the expressions of Gal-3, IκB and p65 were detected by immunohistochemistry. Their relationship with clinical characteristics was analyzed.
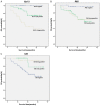
Results: The expression of Gal-3 and p65 was negatively correlated with the overall survival rate (P<0.05), while the expression of IκB was positively correlated with the overall survival rate (P<0.05). Expression of Gal-3, p65 and IκB were found associated with EOC platinum resistance (P<0.05), and expression of Gal-3 and p65 correlated with pathologic grading (P<0.05). IκB and Gal-3 were associated with the recurrence of EOC (P<0.05). IκB may be related to clinical stage (P<0.05). Multivariate analysis results showed that abnormal expression of Gal-3 may be an independent prognostic risk factors for the drug resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy (95% CI=5.336~34.112, P<0.05). The expression of Gal-3, p65, and IκB can be clinical immunohistochemical indicators that determine the prognosis of EOC, but the amount of Gal-3 expression was related to the epithelial ovarian cancer's pathologic type and overall survival, which suggested that Gal-3 can be used as a prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Conclusion: Targeted therapy of Gal-3 may become an effective potential new method against epithelial ovarian cancer.
Keywords: Galectin-3; IκB; clinical prognosis; epithelial ovarian cancer; p65.
IJCEP Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Webb PM, Jordan SJ. Epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;41:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Katabuchi H. Frontiers in ovarian cancer science. Springer; 2017.
-
- Nezhat FR, Apostol R, Nezhat C, Pejovic T. New insights in the pathophysiology of ovarian cancer and implications for screening and prevention. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;213:262–7. - PubMed
-
- Sereni MI, Baldelli E, Gambara G, Deng J, Zanotti L, Bandiera E, Bignotti E, Ragnoli M, Tognon G, Ravaggi A, Meani F, Memo M, Angioli R, Liotta LA, Pecorelli SL, Petricoin E 3rd, Pierobon M. Functional characterization of epithelial ovarian cancer histotypes by drug target based protein signaling activation mapping: implications for personalized cancer therapy. Proteomics. 2015;15:365–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
