Recombinant adenovirus (AdEasy system) mediated exogenous expression of long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) biphasic regulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
- PMID: 32509170
- PMCID: PMC7269984
Recombinant adenovirus (AdEasy system) mediated exogenous expression of long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) biphasic regulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
Abstract
Background: We previously constructed AdEasy system for rapid generation of recombinant adenovirus expressing coding genes. However, it is unclear if AdEasy system could be used for exogenously expression of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). Here we investigated how to overexpress lncRNA H19 with AdEasy system and identified the effect of overexpression H19 on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) osteogenic differentiation.
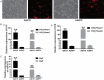
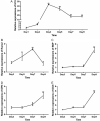
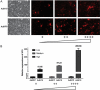
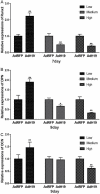
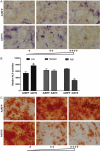
Methods: H19 fragment 1 and H19 fragment 2 were amplified from mouse genomic DNA separately and then connected for full-length H19. H19 was firstly subcloned to homemade pMOK plasmid, then H19 was cut off from pMOK-H19 and subcloned to recombinant adenovirus plasmid. After homologous recombination in AdEasier cells (BJ5183 cell), packing in mammalian packaging cell line and amplification in 293pTP cells, high titer AdH19 was obtained. Immortalized mouse adipose-derived progenitors (iMADs) were infected by AdH19 with different infection rate, the expression of H19, H19 related microRNAs (miRs) and osteogenic differentiation markers were determined by TqPCR. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activities and matrix mineralization were determined by ALP assays and Alizarin red S staining respectively.
Results: AdEasy system was suitable for rapid generation and production of H19, AdH19 can effectively overexpress H19 and serve as functional lncRNA in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Higher dosage of AdH19 inhibited osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, however, lower dosage of AdH19 promoted osteogenic differentiation of MSCs.
Conclusions: We firstly reported the method for the generation of functional lncRNA with AdEasy system, and identified the biphasic effect of H19 on MSCs osteogenic differentiation.
Keywords: AdEasy system; lncRNA H19; mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); osteogenic differentiation.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of the long noncoding RNA H19 in osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jan 21;12(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02149-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33478579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA H19 mediates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) through Notch signaling.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(32):53581-53601. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18655. eCollection 2017 Aug 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881833 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose prevents osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via lncRNA AK028326/CXCL13 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:544-551. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.058. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27693963
-
Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rat ectomesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Dec;22(24):8805-8813. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16648. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30575922
-
The role and mechanism of long non-coding RNA H19 in stem cell osteogenic differentiation.Mol Med. 2021 Aug 12;27(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00350-y. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34384352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic virus: A catalyst for the treatment of gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1017692. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1017692. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs in mesenchymal stromal/stem cells osteogenic differentiation: Implications in osteoarthritis pathogenesis.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Jun 26;14(6):429-434. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i6.429. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35949395 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the long noncoding RNA H19 in osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jan 21;12(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02149-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33478579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of exercise on the expression of long non-coding RNAs in the bone of mice with osteoporosis.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jan;23(1):70. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10993. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 34934441 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA H19 mediates BMP9-induced angiogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by promoting the p53-Notch1 angiogenic signaling axis.Genes Dis. 2022 May 10;10(3):1040-1054. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.04.013. eCollection 2023 May. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37396541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strausberg RL, Levy S, Rogers YH. Emerging DNA sequencing technologies for human genomic medicine. Drug Discov Today. 2008;13:569–577. - PubMed
-
- Chan EY. Advances in sequencing technology. Mutat Res. 2005;573:13–40. - PubMed
-
- Clark MB, Amaral PP, Schlesinger FJ, Dinger ME, Taft RJ, Rinn JL, Ponting CP, Stadler PF, Morris KV, Morillon A, Rozowsky JS, Gerstein MB, Wahlestedt C, Hayashizaki Y, Carninci P, Gingeras TR, Mattick JS. The reality of pervasive transcription. PLoS Biol. 2011;9:e1000625. discussion e1001102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y. Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett. 2013;339:159–166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
