The role of mitochondrial dynamics in human cancers
- PMID: 32509379
- PMCID: PMC7269774
The role of mitochondrial dynamics in human cancers
Abstract
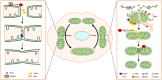
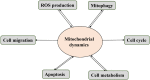
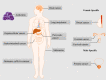
Mitochondria are crucial cellular organelles. Under extracellular stimulations, mitochondria undergo constant fusion and fission dynamics to meet different cellular demands. Mitochondrial dynamics is regulated by specialized proteins and lipids. Dysregulated mitochondrial dynamics has been linked to the initiation and progression of diverse human cancers, affecting aspects such as cancer metastasis, drug resistance and cancer stem cell survival, suggesting that targeting mitochondrial dynamics is a potential therapeutic strategy. In the present review, we summarize the molecular mechanisms underlying fusion and fission dynamics and discuss the effects of mitochondrial dynamics on the development of human cancers.
Keywords: Mitochondrial dynamics; cancer stem cells; human cancers; lipids.
AJCR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Schon EA. A toolkit for the cell’s powerhouse. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:294–296. - PubMed
-
- Brini M. Ca(2+) signalling in mitochondria: mechanism and role in physiology and pathology. Cell Calcium. 2003;34:399–405. - PubMed
-
- Mills EL, Kelly B, O’Neill LAJ. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of immunity. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:488–498. - PubMed
-
- Chan DC. Mitochondrial fusion and fission in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:79–99. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
