Recovery and purification of Aspergillus niger phytase from crude extract using AOT / isooctane reversed micelles
- PMID: 32509541
- PMCID: PMC7264062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00471
Recovery and purification of Aspergillus niger phytase from crude extract using AOT / isooctane reversed micelles
Abstract
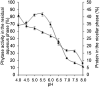
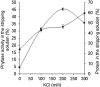
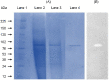
This work describes the successful extraction of Aspergillus niger phytase from a crude extract (CE) obtained from solid-state fermentation by reversed micelle system using anionic surfactant sodium bis (2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate (AOT) in isooctane achieved in two simple steps: forward and backward extractions. The effects of potassium chloride (KCl) concentration, pH of the aqueous solution, and AOT concentration that affect the system were examined. The best result for the forward extraction was obtained with the CE solution at pH 4.0, 50 mM KCl, and 100 mM AOT, while for the backward extraction the best result was achieved with a stripping aqueous solution at pH 5.5 containing 200 mM KCl, achieving a purification factor of 4.03, 1.15 times higher than that reported for the conventional purification process. Phytase purity was demonstrated by SDS-PAGE (89 kDa) and its activity by zymogram, confirming the efficiency of the process with low time consumption (∼40 min).
Keywords: Liquid-liquid extraction; Phytase; Reversed micelles; Triticale.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Song H.-Y., Sheikha A.F.E., Hu D.-M. The positive impacts of microbial phytase on its nutritional applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;86:553–562. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.12.001. - DOI
-
- Kumar V., Sinha A.K., Kajbaf K. Phytic acid and phytase enzyme. Cap 18, pp 467-483. In: Johnson Jodee, Wallace Taylor C., editors. Whole Grains and Their Bioactives: Composition and Health. first edition. © 2019 JohnWiley & Sons Ltd. Published 2019 by JohnWiley & Sons Ltd; 2019.
-
- Neira-Vielma A.A., Aguilar C.N., Ilyina A., Contreras-Esquivel J.C., Carneiro-da-Cunha M.G., Michelena-Álvarez G., Martínez-Hernández J.L. Purification and biochemical characterization of an Aspergillus niger phytase produced by solid-state fermentation using triticale residues as substrate. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018;17:49–54. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2017.12.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhavsar K., Kumar V.R., Khire J.M. Downstream processing of extracellular phytase from Aspergillus Niger: Chromatography process vs. aqueous two phase extraction for its simultaneous partitioning and purification. Process Biochem. 2012;47:1066–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2012.03.012. - DOI
-
- El Aferni A., Guettari M. T. determination of the water/AOT/isooctane reverse micelles size parameters from their refractive index datatajouri. J. Solution Chem. 2017 doi: 10.1007/s10953-016-0563-x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
