Modulatory Effect of Serotonergic System in Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures and Associated Memory Deficit: Role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/2C
- PMID: 32509547
- PMCID: PMC7251343
- DOI: 10.14581/jer.19012
Modulatory Effect of Serotonergic System in Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures and Associated Memory Deficit: Role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/2C
Abstract
Background and purpose: Recent studies have recognised the memory deficit as one of the most common psychiatric issues in the patients with epilepsy, which severely affects the quality of life. Our previous studies have demonstrated the possible involvement of serotonergic system in the pathogenesis of epilepsy and associated memory deficit. The possible involvement of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/2C receptor has not been explored yet. Therefore, this study has been envisaged to explore the effect of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/2C receptor modulation on epilepsy and memory deficit in pentylenetetrazole-kindled mice.
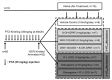
Methods: In the present experimental approach, we examined the efficacy of modulation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/2C receptor in pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling in male Swiss mice (n=75). Mice were kindled by sub-convulsive dose of pentylenetetrazole (35 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection), at the interval of 48±2 hours). Successfully kindled animals were treated with 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A/2C receptor modulators. The effect of different treatments on seizure severity score and memory impairment was analysed.
Results: 5-HT1A receptor agonist improved the memory functions while seizure severity was not improved, and the opposite effect was observed with 5-HT1A receptor antagonist. On the other hand, 5-HT2A/2C receptor agonist significantly improved memory deficit as well as seizure severity in the kindled animals.
Conclusions: The outcome of the study indicates the possible involvement of 5-HT2A/2C receptor in the pathogenesis of epilepsy and associated memory deficit, which can be further explored for its management.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Epilepsy; Kindling; Memory disorders; Pentylenetetrazole; Receptor; Serotonin.
Copyright © 2019 Korean Epilepsy Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kambaja B, Dupont S. Amnesia, memory disturbances and epilepsy. Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil. 2016;14:415–9. - PubMed
-
- Mishra A, Goel RK. Age dependent learning and memory deficit in Pentylenetetrazol kindled mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;674:315–20. - PubMed
-
- Mishra A, Goel RK. Psychoneurochemical investigations to reveal neurobiology of memory deficit in epilepsy. Neurochem Res. 2013;38:2503–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

