Periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics: A perio-ortho ambidextrous perspective
- PMID: 32509685
- PMCID: PMC7266211
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1055_19
Periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics: A perio-ortho ambidextrous perspective
Abstract
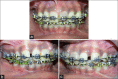
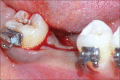
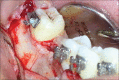
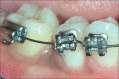
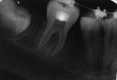
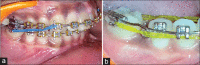
The interdisciplinary collaboration of periodontics and orthodontics has allowed teeth to be moved 2-3 times faster, reducing the time required for traditional orthodontic therapy considerably. Periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics (PAOO), also known as Wilckodontics, is a combination of a selective decortication facilitated orthodontics and alveolar augmentation. With this technique, there is no dependence on the pre-existing alveolar volume. This case report describes the treatment of permanent mandibular molar protraction in a 14-year-old patient undergoing orthodontic therapy using PAOO with piezosurgery.
Keywords: Corticotomy; bone grafts; orthodontics; osteogenic; periodontics.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



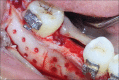
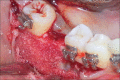
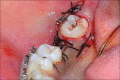
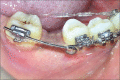
References
-
- Pathak TS, Kini V, Kanagotagi S, Balasubramanian K, Gupta H. Wilckodontics. J Contemp Dent. 2013;3:15–9.
-
- Wilcko T, Wilcko W. An evidence-based analysis of periodontally accelerated orthodontic and osteogenic techniques:A synthesis of scientific perspectives semin. Orthod. 2008;14:305–16.
-
- Frost HM. The biology of fracture healing:An overview for clinicians. Part II. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1989;248:283–9. - PubMed
-
- Köle H. Surgical operations of the alveolar ridge to correct occlusal abnormalities. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989;12:515–29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
