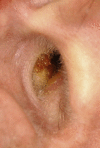
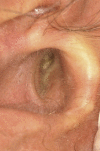
Unusual external auditory canal relapse in pemphigus vulgaris
- PMID: 32509944
- PMCID: PMC7263999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.04.014
Unusual external auditory canal relapse in pemphigus vulgaris
Keywords: DSG, desmogleins; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ENT, ear, nose, and throat; PV, pemphigus vulgaris; autoimmune bullous disease; dermatology; ear; nose and throat; otoscopy; pemphigus vulgaris.
Figures
References
-
- Spindler V., Eming R., Schmidt E. Mechanisms causing loss of keratinocyte cohesion in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Fawzy M.M., Hegazy R.A., Abdel Fattah A.F. Ear, nose, and throat involvement in Egyptian patients with pemphigus vulgaris: a step towards a better management. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1268–1273. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed A.R., Spigelman Z., Cavacini L.A., Posner M.R. Treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with rituximab and intravenous immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1772–1779. - PubMed
-
- Bilgic-Teme A., Cem Temel I., Bostancı-Toptas A., Turhan M., Bozkurt S., Uzun S. Evaluation of ear, nose, and throat involvement in pemphigus vulgaris in comparison with pemphigus severity scoring systems: a cross-sectional study. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018;26:283–288. - PubMed
-
- Ohki M., Kikuchi S. Nasal, oral, and pharyngolaryngeal manifestations of pemphigus vulgaris: endoscopic ororhinolaryngologic examination. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017;96:120–127. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous