This is a preprint.
A Single and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Molecular Test for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) at Home, Clinic, and Points of Entry
- PMID: 32511284
- PMCID: PMC7251958
- DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.11860137.v1
A Single and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Molecular Test for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) at Home, Clinic, and Points of Entry
Update in
-
Single- and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Point-of-Care, Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Anal Chem. 2021 Sep 28;93(38):13063-13071. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03016. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34541844 Free PMC article.
Abstract
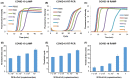
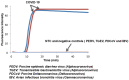
The 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is a newly emerged strain that has never been found in humans before. At present, the laboratory-based reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is the main method to confirm COVID-19 infection. The intensification of the COVID-19 epidemic overwhelms limited clinical resources in particular, but not only, in developing countries, resulting in many patients not being tested for the infection and in large queues of potentially infected individuals waiting to be tested while providing a breeding ground for the disease. We describe here a rapid, highly sensitive, point-of-care, molecular test amenable for use at home, in the clinic, and at points of entry by minimally trained individuals and with minimal instrumentation. Our test is based on loop mediated isothermal amplification (COVID-19 LAMP) and for higher sensitivity on nested nucleic acid, two stage isothermal amplification (COVID-19 Penn-RAMP). Both tests can be carried out in closed tubes with either fluorescence or colorimetric (e.g., leuco crystal violet LCV) detection. COVID-19 LAMP performs on par with COVID-19 RT-PCR. COVID-19 RAMP has 10 fold better sensitivity than COVID-19 LAMP and COVID-19 RT-PCR when testing purified targets and 100 times better sensitivity than COVID-19 LAMP and COVID-19 RT-PCR when testing rapidly prepared sample mimics. Due to fortunate scarcity of COVID-19 infections in the USA, we were not able to test our assays and methods with patient samples. We hope that such tests will be carried out by colleagues in impacted countries. Our Closed-Tube Penn-RAMP has the potential to significantly reduce false negatives while being amenable to use with minimal instrumentation and training.
Keywords: COVID-19; Isothermal amplification; RAMP; Two stage,; closed-tube; nested amplification.
Conflict of interest statement
University of Pennsylvania has applied for a patent on Penn-RAMP with J.S. and H.H.B. listed as co-inventors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single- and Two-Stage, Closed-Tube, Point-of-Care, Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Anal Chem. 2021 Sep 28;93(38):13063-13071. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03016. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34541844 Free PMC article.
-
Two stage, nested isothermal amplification in a single tube.Analyst. 2021 Feb 21;146(4):1311-1319. doi: 10.1039/d0an01835j. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Analyst. 2021. PMID: 33367323 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite Clinical Validation of Isothermal Amplification-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Assays Using Different Sampling Strategies.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0084621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00846-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34668736 Free PMC article.
-
Progression of LAMP as a Result of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Is PCR Finally Rivaled?Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 6;12(7):492. doi: 10.3390/bios12070492. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): A Rapid, Sensitive, Specific, and Cost-Effective Point-of-Care Test for Coronaviruses in the Context of COVID-19 Pandemic.Biology (Basel). 2020 Jul 22;9(8):182. doi: 10.3390/biology9080182. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32707972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Presence and stability of SARS-CoV-2 on environmental currency and money cards in Utah reveals a lack of live virus.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 25;17(1):e0263025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263025. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35077511 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-disciplinary approaches to assist with nucleic acid testing for SARS-CoV-2.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Aug;105(16-17):6291-6299. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11498-2. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34423408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Advances in diagnostic tools, treatment strategies, and vaccine development.J Biosci. 2020;45(1):148. doi: 10.1007/s12038-020-00114-6. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33410425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) assay for on-site diagnosis of SARS CoV-2.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 3;16(3):e0248042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248042. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33657176 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in public workspace environments.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 24;16(2):e0240524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240524. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33626039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeng ZQ, Chen DH, Tan WP, Qiu SY, Xu D, Liang HX, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of human coronaviruses oc43, 229e, nl63, and hku1: A study of hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infection in guangzhou, china. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2018;37:363–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World health organization. (2003). Consensus document on the epidemiology of severe acute respiratory syndrome (sars). World health organization; Https://apps.Who.Int/iris/handle/10665/70863.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
