This is a preprint.
All-in-One Dual CRISPR-Cas12a (AIOD-CRISPR) Assay: A Case for Rapid, Ultrasensitive and Visual Detection of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and HIV virus
- PMID: 32511323
- PMCID: PMC7239053
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.03.19.998724
All-in-One Dual CRISPR-Cas12a (AIOD-CRISPR) Assay: A Case for Rapid, Ultrasensitive and Visual Detection of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and HIV virus
Update in
-
Ultrasensitive and visual detection of SARS-CoV-2 using all-in-one dual CRISPR-Cas12a assay.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 18;11(1):4711. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18575-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32948757 Free PMC article.
Abstract
A recent outbreak of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19, has spread rapidly all over the world. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is another deadly virus and causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Rapid and early detection of these viruses will facilitate early intervention and reduce disease transmission risk. Here, we present an All-In-One Dual CRISPR-Cas12a (termed "AIOD-CRISPR") assay method for simple, rapid, ultrasensitive, one-pot, and visual detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and HIV virus. In our AIOD CRISPR assay, a pair of crRNAs was introduced to initiate dual CRISPR-Cas12a detection and improve detection sensitivity. The AIOD-CRISPR assay system was successfully utilized to detect nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) of SARS-CoV-2 and HIV with a sensitivity of few copies. Also, it was evaluated by detecting HIV-1 RNA extracted from human plasma samples, achieving a comparable sensitivity with real-time RT-PCR method. Thus, our method has a great potential for developing next-generation point-of-care molecular diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures University of Connecticut has filed a patent application on the methods described, and Changchun Liu and Xiong Ding are named as inventors.
Figures





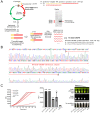
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-58. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... (2020).
-
- WHO. HIV/AIDS data and statistics. https://www.who.int/hiv/data/en/. (2019).
-
- Cao L, et al. Advances in digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) and its emerging biomedical applications. Biosens Bioelectron 90, 459–474 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
