This is a preprint.
Shotgun Transcriptome and Isothermal Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Reveals Unique Host Responses, Viral Diversification, and Drug Interactions
- PMID: 32511352
- PMCID: PMC7255793
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.04.20.048066
Shotgun Transcriptome and Isothermal Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Reveals Unique Host Responses, Viral Diversification, and Drug Interactions
Update in
-
Shotgun transcriptome, spatial omics, and isothermal profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals unique host responses, viral diversification, and drug interactions.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 12;12(1):1660. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21361-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33712587 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused thousands of deaths worldwide, including >18,000 in New York City (NYC) alone. The sudden emergence of this pandemic has highlighted a pressing clinical need for rapid, scalable diagnostics that can detect infection, interrogate strain evolution, and identify novel patient biomarkers. To address these challenges, we designed a fast (30-minute) colorimetric test (LAMP) for SARS-CoV-2 infection from naso/oropharyngeal swabs, plus a large-scale shotgun metatranscriptomics platform (total-RNA-seq) for host, bacterial, and viral profiling. We applied both technologies across 857 SARS-CoV-2 clinical specimens and 86 NYC subway samples, providing a broad molecular portrait of the COVID-19 NYC outbreak. Our results define new features of SARS-CoV-2 evolution, nominate a novel, NYC-enriched viral subclade, reveal specific host responses in interferon, ACE, hematological, and olfaction pathways, and examine risks associated with use of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers. Together, these findings have immediate applications to SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics, public health, and new therapeutic targets.
Keywords: RNA-seq; coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); global health; loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP); next-generation sequencing (NGS); quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Nathan Tanner and Bradley W. Langhorst are employees at New England Biolabs.
Figures
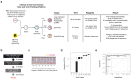
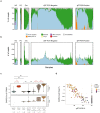

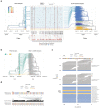
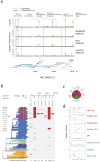
References
-
- Agata J, Ura N, Yoshida H, Shinshi Y, Sasaki H, Hyakkoku M, Taniguchi S, Shimamoto K. Olmesartan Is an Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker with an Inhibitory Effect on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Hypertension Research 29, 865–874 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Ajioka RS, Phillips JD, Kushner JP. Biosynthesis of heme in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. July;1763(7):723–36 - PubMed
-
- Amanat F, Nguyen T, Chromikova V, Strohmeier S, Stadlbauer D, Javier A, Jiang K, Asthagiri-Arunkumar G, Polanco J, Bermudez-Gonzalez M, Caplivski D, Cheng A, Kedzierska K, Vapalahti O, Hepojoki J, Simon V, Krammer F. A serological assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. MedRxiv. 2020. March 18 https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.17.20037713v1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews S. FASTQC A Quality Control tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Babraham Inst. (2015).
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (1995)
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
