This is a preprint.
An OpenData portal to share COVID-19 drug repurposing data in real time
- PMID: 32511420
- PMCID: PMC7276055
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.06.04.135046
An OpenData portal to share COVID-19 drug repurposing data in real time
Abstract
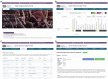
The National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) has developed an online open science data portal for its COVID-19 drug repurposing campaign - named OpenData - with the goal of making data across a range of SARS-CoV-2 related assays available in real-time. The assays developed cover a wide spectrum of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle, including both viral and human (host) targets. In total, over 10,000 compounds are being tested in full concentration-response ranges from across multiple annotated small molecule libraries, including approved drug, repurposing candidates and experimental therapeutics designed to modulate a wide range of cellular targets. The goal is to support research scientists, clinical investigators and public health officials through open data sharing and analysis tools to expedite the development of SARS-CoV-2 interventions, and to prioritize promising compounds and repurposed drugs for further development in treating COVID-19.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
