This is a preprint.
A High Through-put Assay for Circulating Antibodies Directed against the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus 2
- PMID: 32511609
- PMCID: PMC7276036
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.04.14.20059501
A High Through-put Assay for Circulating Antibodies Directed against the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus 2
Update in
-
A High-Throughput Assay for Circulating Antibodies Directed Against the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2.J Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 13;222(10):1629-1634. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa531. J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32860510 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: More than one million infections with the severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have been confirmed. While PCR-based assays are used for diagnosis, high through-put serologic methods are needed to detect antibodies for seroserveillance and for identification of seroconversion, potential plasma donors, and the nature of the immune response to this pathogen.
Methods: A Luminex binding assay was used to assess the presence of antibodies in human sera from COVID-19-infected and -uninfected individuals specific for two recombinant proteins of SARS-CoV-2.
Findings: Fluorochrome-labeled beads were coated with a recombinant soluble stabilized trimeric SARS-CoV-2 S protein ectodomain or its central portion, the receptor binding domain (RBD). Coated beads were incubated with sera, followed by incubation with biotinylated anti-human total Ig antibodies and phycoerythrin (PE)-labeled streptavidin. Readout using a Luminex analyzer clearly differentiated between sera of the infected and uninfected subject, delineating a wide range of serum antibody levels in infected subjects.
Interpretation: Antibody assays of sera can identify individuals who are infected with SARS-CoV-2 and have seroconverted, as well as subjects who have been infected and recovered. The use of the Luminex binding Ab assay has the advantage that it can be run in approximately 2.5 hours, uses very little antigen, and permits a high through-put of samples/day.
Funding: NIAID contracts and grants, Department of Veterans Affairs grants, the Microbiology Laboratory Clinical Services, Translational Science Hub, and Personalized Virology Initiative, and Department of Medicine of Mount Sinai Health System and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
None of the authors currently have a financial interest or personal relationships personal relationships that would constitute a conflict of interest such as rivalries, academic competition, or intellectual beliefs with other people or organizations. The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has decided it will submit a patent application based on the method described herein.
Figures
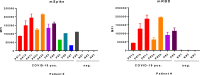


References
-
- Storch GA. Diagnostic Virology. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2000; 31: 739–751, 2000. - PubMed
-
- The Antibody Initiative: Diagnosing Disease with Antibodies. National Museum of American History, Behring Collection; https://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/object-groups/antibody-initia...
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
