Prevention of preeclampsia
- PMID: 32513597
- PMCID: PMC8236336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.siny.2020.101123
Prevention of preeclampsia
Abstract
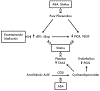
Preeclampsia is an obstetric disorder that affects 3-8% of pregnant women and remains a leading cause of short- and long-term neonatal and maternal morbidity and mortality. Professional societies recommend the use of low dose aspirin to prevent preeclampsia in high-risk women. However, interest in prevention of this disease and better understanding of its pathophysiology have led to growing research on other agents. This review focuses on the main therapeutic agents evaluated or in use for preeclampsia prevention.
Keywords: Aspirin; Esomeprazole; Metformin; Preeclampsia; Pregnancy; Statin.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Geographic variation in the incidence of hypertension in pregnancy. World Health Organization International Collaborative Study of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158(1):80–3. - PubMed
-
- Firoz T, Sanghvi H, Merialdi M, Von Dadelszen P. Pre-eclampsia in low and middle income countries. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25:537–48. - PubMed
-
- Espinoza J, Vidaeff A, Pettker CM, Simhan H. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(1):e1–25. - PubMed
-
- Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;133(1):e1–25. - PubMed
-
- Barton JR, Sibai BM. Prediction and prevention of recurrent preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:359–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

