H1 linker histones silence repetitive elements by promoting both histone H3K9 methylation and chromatin compaction
- PMID: 32513732
- PMCID: PMC7322038
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1920725117
H1 linker histones silence repetitive elements by promoting both histone H3K9 methylation and chromatin compaction
Abstract
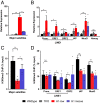
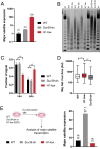
Nearly 50% of mouse and human genomes are composed of repetitive sequences. Transcription of these sequences is tightly controlled during development to prevent genomic instability, inappropriate gene activation and other maladaptive processes. Here, we demonstrate an integral role for H1 linker histones in silencing repetitive elements in mouse embryonic stem cells. Strong H1 depletion causes a profound de-repression of several classes of repetitive sequences, including major satellite, LINE-1, and ERV. Activation of repetitive sequence transcription is accompanied by decreased H3K9 trimethylation of repetitive sequence chromatin. H1 linker histones interact directly with Suv39h1, Suv39h2, and SETDB1, the histone methyltransferases responsible for H3K9 trimethylation of chromatin within these regions, and stimulate their activity toward chromatin in vitro. However, we also implicate chromatin compaction mediated by H1 as an additional, dominant repressive mechanism for silencing of repetitive major satellite sequences. Our findings elucidate two distinct, H1-mediated pathways for silencing heterochromatin.
Keywords: chromatin; epigenetics; linker histones; repetitive elements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Silencing the genome with linker histones.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 7;117(27):15388-15390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009513117. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32561644 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Misteli T., Gunjan A., Hock R., Bustin M., Brown D. T., Dynamic binding of histone H1 to chromatin in living cells. Nature 408, 877–881 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Woodcock C. L., Skoultchi A. I., Fan Y., Role of linker histone in chromatin structure and function: H1 stoichiometry and nucleosome repeat length. Chromosome Res. 14, 17–25 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T., Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128, 693–705 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Happel N., Doenecke D., Histone H1 and its isoforms: Contribution to chromatin structure and function. Gene 431, 1–12 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

