mcr-1 Gene Expression Modulates the Inflammatory Response of Human Macrophages to Escherichia coli
- PMID: 32513853
- PMCID: PMC7375756
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00018-20
mcr-1 Gene Expression Modulates the Inflammatory Response of Human Macrophages to Escherichia coli
Abstract
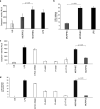
MCR-1 is a plasmid-encoded phosphoethanolamine transferase able to modify the lipid A structure. It confers resistance to colistin and was isolated from human, animal, and environmental strains of Enterobacteriaceae, raising serious global health concerns. In this paper, we used recombinant mcr-1-expressing Escherichia coli to study the impact of MCR-1 products on E. coli-induced activation of inflammatory pathways in activated THP-1 cells, which was used as a model of human macrophages. We found that infection with recombinant mcr-1-expressing E. coli significantly modulated p38-MAPK and Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) activation and pNF-κB nuclear translocation as well as the expression of genes for the relevant proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-12 (IL-12), and IL-1β compared with mcr-1-negative strains. Caspase-1 activity and IL-1β secretion were significantly less activated by mcr-1-positive E. coli strains than the mcr-1-negative parental strain. Similar results were obtained with clinical isolates of mcr-1-positive E. coli, suggesting that, in addition to colistin resistance, the expression of mcr-1 allows the escape of early host innate defenses and may promote bacterial survival.
Keywords: MCR-1; cytokines; inflammation; macrophages.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Cannatelli A, Giani T, Aiezza N, Di Pilato V, Principe L, Luzzaro F, Galeotti CL, Rossolini GM. 2017. An allelic variant of the PmrB sensor kinase responsible for colistin resistance in an Escherichia coli strain of clinical origin. Sci Rep 7:5071. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-05167-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourrel AS, Poirel L, Royer G, Darty M, Vuillemin X, Kieffer N, Clermont O, Denamur E, Nordmann P, Decousser J-W; IAME Resistance Group. 2019. Colistin resistance in Parisian inpatient faecal Escherichia coli as the result of two distinct evolutionary pathways. J Antimicrob Chemother 74:1521–1530. doi:10.1093/jac/dkz090. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

