A Public Health Laboratory Response to the Pandemic
- PMID: 32513860
- PMCID: PMC7383562
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01110-20
A Public Health Laboratory Response to the Pandemic
Abstract
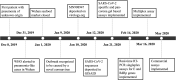
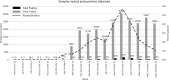
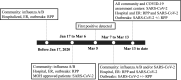
An outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by a novel coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 [SARS-CoV-2]) began in Wuhan, Hubei, China, in December 2019 and spread rapidly worldwide. The response by the Alberta Precision Laboratories, Public Health Laboratory (ProvLab), AB, Canada, included the development and implementation of nucleic acid detection-based assays and dynamic changes in testing protocols for the identification of cases as the epidemic curve increased exponentially. This rapid response was essential to slow down and contain transmission and provide valuable time to the local health authorities to prepare appropriate response strategies. As of May 24, 2020, 236,077 specimens were tested, with 6,475 (2.74%) positives detected in the province of Alberta, Canada. Several commercial assays are now available; however, the response from commercial vendors to develop and market validated tests is a time-consuming process. In addition, the massive global demand made it difficult to secure a reliable commercial supply of testing kits and reagents. A public health laboratory serves a unique and important role in the delivery of health care. One of its functions is to anticipate and prepare for novel emerging pathogens with a plan for pandemic preparedness. Here, we outline the response that involved the development and deployment of testing methodologies that evolved as SARS-CoV-2 spread worldwide, the challenges encountered, and mitigation strategies. We also provide insight into the organizational structure of how a public health response is coordinated in Alberta, Canada, and its benefits.
Keywords: COVID-19; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2; public health.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, Ren R, Leung KSM, Lau EHY, Wong JY, Xing X, Xiang N, Wu Y, Li C, Chen Q, Li D, Liu T, Zhao J, Liu M, Tu W, Chen C, Jin L, Yang R, Wang Q, Zhou S, Wang R, Liu H, Luo Y, Liu Y, Shao G, Li H, Tao Z, Yang Y, Deng Z, Liu B, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Shi G, Lam TTY, Wu JT, Gao GF, Cowling BJ, Yang B, Leung GM, Feng Z. 2020. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med 382:1199–1207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. 2020. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. 2020. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382:727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

