Septic Shock and Purpura Fulminans Due to Streptococcus pneumoniae Bacteremia in an Unvaccinated Immunocompetent Adult: Case Report and Review
- PMID: 32513908
- PMCID: PMC7304654
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.923266
Septic Shock and Purpura Fulminans Due to Streptococcus pneumoniae Bacteremia in an Unvaccinated Immunocompetent Adult: Case Report and Review
Abstract
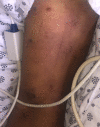
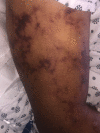
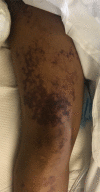
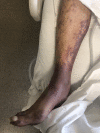
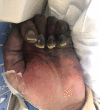
BACKGROUND Despite proven efficacy of vaccinations against Streptococcus pneumoniae in preventing infection, only 70% of eligible individuals receive the vaccine in the United States. Pneumococcal bacteremia represents a form of invasive pneumococcal disease and is associated with high mortality, especially in immunocompromised patients and the elderly. Purpura fulminans is a rare complication and manifestation of disseminated intravascular coagulation and sepsis. It is exceedingly rare in the setting of pneumococcal bacteremia, particularly in immunocompetent individuals. CASE REPORT We report a generally healthy 67-year-old male with schizophrenia who refused pneumococcal vaccination. He had an intact and functional spleen with a functional immune system. The patient presented with fever and diarrhea. He subsequently progressed to develop purpura fulminans and septic shock due to S. pneumoniae bacteremia. Despite an extensive search for the primary source of infection, none could not be identified. Due to timely initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy and aggressive supportive care in an intensive care unit, he recovered despite multi-organ failure that developed throughout his hospitalization. CONCLUSIONS We present a rare manifestation of a potentially preventable disease and emphasize the importance of pneumococcal vaccination in order to decrease the risk of developing invasive pneumococcal disease. Furthermore, we discuss etiology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and evidence-based management of purpura fulminans and invasive pneumococcal disease with a literature review. Purpura fulminans due to S. pneumoniae is exceedingly rare in immunocompetent patients and an unusual clinical manifestation of pneumococcal bacteremia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Purpura Fulminans: A rare presentation of Streptococcus Pneumoniae infection.BMJ Case Rep. 2017 Oct 20;2017:bcr2017221150. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221150. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29054893 Free PMC article.
-
Purpura fulminans due to Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteraemia in an unsplectomised immunocompetent adult without primary hypocomplementaemia.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 May 19;15(5):e249514. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2022-249514. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589268 Free PMC article.
-
Septic shock and purpura fulminans secondary to Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteraemia in an immunocompetent individual.BMJ Case Rep. 2025 Mar 19;18(3):e263010. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2024-263010. BMJ Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40107740
-
Purpura fulminans associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae septicemia in an asplenic pediatric patient.Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013 Sep;104(7):623-7. doi: 10.1016/j.adengl.2012.05.027. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013. PMID: 23985086 Review.
-
Purpura fulminans in pneumococcal sepsis: case report and review.Scand J Infect Dis. 1997;29(5):479-83. doi: 10.3109/00365549709011858. Scand J Infect Dis. 1997. PMID: 9435036 Review.
Cited by
-
The Many Faces of Purpura: Vancomycin-Induced Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis.Case Rep Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 4;2021:9932425. doi: 10.1155/2021/9932425. eCollection 2021. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34194855 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Sets of Autoantibodies Induced by SARS-CoV-2, Adenovirus and Bacterial Antigens Cross-React with Human Blood Protein Antigens in COVID-19 Coagulopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11500. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911500. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232795 Free PMC article.
-
Right Lower Extremity Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens Due to Iliotibial Vein Thrombosis With Compartment Syndrome and Circulatory Shock: Case Report and Review.Cureus. 2022 Dec 9;14(12):e32364. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32364. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36628047 Free PMC article.
-
L-Thyroxine and L-thyroxine-based antimicrobials against Streptococcus pneumoniae and other Gram-positive bacteria.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 22;10(7):e27982. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27982. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38689973 Free PMC article.
-
In-hospital survival paradox in patients with sleep apnea-A nation-wide nested case-control study.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 21;17(7):e0271004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271004. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35862391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pneumococcal Disease, Clinical| Features, CDC. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/pneumococcal/clinicians/clinical-features.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

