Interferon-mediated reprogramming of membrane cholesterol to evade bacterial toxins
- PMID: 32514064
- PMCID: PMC7778040
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-0695-4
Interferon-mediated reprogramming of membrane cholesterol to evade bacterial toxins
Abstract
Plasma membranes of animal cells are enriched for cholesterol. Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs) are pore-forming toxins secreted by bacteria that target membrane cholesterol for their effector function. Phagocytes are essential for clearance of CDC-producing bacteria; however, the mechanisms by which these cells evade the deleterious effects of CDCs are largely unknown. Here, we report that interferon (IFN) signals convey resistance to CDC-induced pores on macrophages and neutrophils. We traced IFN-mediated resistance to CDCs to the rapid modulation of a specific pool of cholesterol in the plasma membrane of macrophages without changes to total cholesterol levels. Resistance to CDC-induced pore formation requires the production of the oxysterol 25-hydroxycholesterol (25HC), inhibition of cholesterol synthesis and redistribution of cholesterol to an esterified cholesterol pool. Accordingly, blocking the ability of IFN to reprogram cholesterol metabolism abrogates cellular protection and renders mice more susceptible to CDC-induced tissue damage. These studies illuminate targeted regulation of membrane cholesterol content as a host defense strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
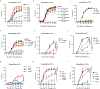






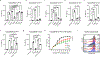




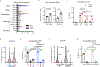

Comment in
-
Cholesterol in quarantine.Nat Immunol. 2020 Jul;21(7):716-717. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0712-7. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32514065 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lange Y, Swaisgood MH, Ramos BV & Steck TL Plasma membranes contain half the phospholipid and 90% of the cholesterol and sphingomyelin in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 264, 3786–3793 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Ikonen E Cellular cholesterol trafficking and compartmentalization. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 9, 125–138 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Luo J, Yang H & Song BL Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21, 225–245 (2020). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Bligh EG & Dyer WJ A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37, 911–917 (1959). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

