Amikacin pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic in intensive care unit: a prospective database
- PMID: 32514769
- PMCID: PMC7276966
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-020-00685-5
Amikacin pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic in intensive care unit: a prospective database
Abstract
Background: Aminoglycosides have a concentration-dependent therapeutic effect when peak serum concentration (Cmax) reaches eight to tenfold the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC). With an amikacin MIC of 8 mg/L, the Cmax should be 64-80 mg/L. This objective is based on clinical breakpoints and not on measured MIC. This study aimed to assess the proportion of patients achieving the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) target Cmax/MIC ≥ 8 using the measured MIC in critically ill patients treated for documented Gram-negative bacilli (GNB) infections.
Methods: Retrospective analysis from February 2016 to December 2017 of a prospective database conducted in 2 intensive care units (ICU). All patients with documented severe GNB infections treated with amikacin (single daily dose of 25 mg/kg of total body weight (TBW)) with both MIC and Cmax measurements at first day of treatment (D1) were included. Results are expressed in n (%) or median [min-max].
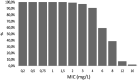
Results: 93 patients with 98 GNB-documented infections were included. The median Cmax was 55.2 mg/L [12.2-165.7] and the median MIC was 2 mg/L [0.19-16]. Cmax/MIC ratio ≥ 8 was achieved in 87 patients (88.8%) while a Cmax ≥ 64 mg/L was achieved in only 38 patients (38.7%). Overall probability of PK/PD target attainment was 93%. No correlation was found between Cmax/MIC ratio and clinical outcome at D8 and D28.
Conclusion: According to PK/PD parameters observed in our study, single daily dose of amikacin 25 mg/kg of TBW appears to be sufficient in most critically ill patients treated for severe GNB infections.
Keywords: Amikacin; Intensive care unit; Pharmacodynamic; Pharmacokinetic.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. MONTRAVERS reports personal fees and non-financial support from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Basilea, Bayer, Cubist, Menarini, MSD, Parexel, Pfizer, Tetraphase and The Medicines Company unrelated to the submitted work. Dr PAJOT reports personal fees from MSD unrelated to the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
-
- EUCAST. Aminoglycosides: http://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_t....
-
- ANSM. Bon usage des aminosides administrés par voie injectable: gentamicine, tobramycine, netilmicine, amikacine – Mise au point 2011.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources