Members of Prevotella Genus Distinctively Modulate Innate Immune and Barrier Functions in a Human Three-Dimensional Endometrial Epithelial Cell Model
- PMID: 32515473
- PMCID: PMC7661762
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa324
Members of Prevotella Genus Distinctively Modulate Innate Immune and Barrier Functions in a Human Three-Dimensional Endometrial Epithelial Cell Model
Abstract
Background: Prevotella species are commonly isolated from the reproductive tract of women with obstetric/gynecologic health complications. However, contributions of this genus to changes in local microenvironment are not well characterized. Our objective was to evaluate species-specific effects of Prevotella on the human endometrial epithelium.
Methods: Thirteen Prevotella strains, originally isolated from the human oral cavity, amniotic fluid, endometrium, or vagina (including women with bacterial vaginosis), were obtained from BEI and ATCC resources. Bacteria were evaluated in silico and in vitro using human endometrial epithelial cells (EEC) grown as monolayers or a 3-dimensional (3D) model.
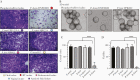
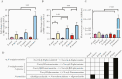
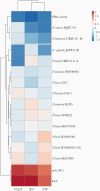
Results: Genomic characterization illustrated metabolic and phylogenetic diversity of Prevotella genus. Among tested species, P. disiens exhibited cytotoxicity. Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the 3D EEC model revealed species-specific colonization patterns and alterations of ultracellular structures. Infection with sialidase-producing P. timonensis resulted in elongated microvilli, and increased MUC3 and MUC4 expression. Infections with Prevotella species, including P. bivia, did not result in significant proinflammatory activation of EEC.
Conclusions: Collectively, findings indicate that Prevotella species are metabolically diverse and overall not cytotoxic or overtly inflammatory in EEC; however, these bacteria can form biofilms, alter barrier properties of the endometrial epithelium, and ultimately impact colonization of secondary colonizers.
Keywords: ascending infection; bacterial vaginosis; biofilm; colonizer; epithelial layer; genital inflammation; membrane-associated mucin; pathway prediction; sialidase; upper reproductive tract infection.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Takahashi N. Microbial ecosystem in the oral cavity: metabolic diversity in an ecological niche and its relationship with oral diseases. Int Congr Ser 2005; 1284:103–12.
-
- Di Cicco M, Pistello M, Jacinto T, et al. Does lung microbiome play a causal or casual role in asthma? Pediatr Pulmonol 2018; 53:1340–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

