Identification of HER2-Positive Metastases in Patients with HER2-Negative Primary Breast Cancer by Using HER2-targeted 89Zr-Pertuzumab PET/CT
- PMID: 32515679
- PMCID: PMC7543717
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020192828
Identification of HER2-Positive Metastases in Patients with HER2-Negative Primary Breast Cancer by Using HER2-targeted 89Zr-Pertuzumab PET/CT
Abstract
Background Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-targeted therapies are successful in patients with HER2-positive malignancies; however, spatial and temporal heterogeneity of HER2 expression may prevent identification of optimal patients for these therapies. Purpose To determine whether imaging with the HER2-targeted PET tracer zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab can depict HER2-positive metastases in women with HER2-negative primary breast cancer. Materials and Methods From January to June 2019, women with biopsy-proven HER2-negative primary breast cancer and biopsy-proven metastatic disease were enrolled in a prospective clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02286843) and underwent 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT for noninvasive whole-biopsy evaluation of potential HER2-positive metastases. 89Zr-pertuzumab-avid foci that were suspicious for HER2-positive metastases were tissue sampled and examined by pathologic analysis to document HER2 status. Results Twenty-four women (mean age, 55 years ± 11 [standard deviation]) with HER2-negative primary breast cancer were enrolled. Six women demonstrated foci at 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT that were suspicious for HER2-positive disease. Of these six women, three had biopsy-proven HER2-positive metastases, two had pathologic findings that demonstrated HER2-negative disease, and one had a fine-needle aspirate with inconclusive results. Conclusion Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-targeted imaging with zirconium 89-pertuzumab PET/CT was successful in detecting HER2-positive metastases in women with HER2-negative primary breast cancer. This demonstrates the ability of targeted imaging to identify patients for targeted therapies that might not otherwise be considered. © RSNA, 2020 Online supplemental material is available for this article. See the editorial by Mankoff and Pantel in this issue.
Figures

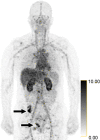
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/6a54f345b8b3/radiol.2020192828.fig1a.gif)
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/7e9c3acc6460/radiol.2020192828.fig1b.gif)
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/723e4af885d3/radiol.2020192828.fig1c.gif)
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/76b0905d48e8/radiol.2020192828.fig1d.gif)
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/a6891f539e5e/radiol.2020192828.fig1e.gif)
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/54972a77f9e9/radiol.2020192828.fig1f.gif)
![Identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastases in a 66-year-old woman with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted zirconium 89 (89Zr)-pertuzumab PET/CT. (a) HER2 immunohistochemistry of the primary breast malignancy at 200× magnification was 1+ (faint staining, arrow), consistent with HER2-negative malignancy. (b) Maximum intensity projection image from research 89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT demonstrates multiple osseous and hepatic foci, suspicious for HER2-positive malignancy (arrows show hepatic [standardized uptake value, 18.1] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 16.5] reference lesions). (c) Axial CT image in patient in prone position acquired from a CT-guided biopsy of an 89Zr-pertuzumab–avid osseous focus. (d) HER2 immunohistochemistry at 200× magnification of the biopsied lesion was 2+ (moderate staining, arrow); 2+ HER2 immunohistochemistry is considered equivocal and thus HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed. (e) HE (CEP17) copy number 3.07, and HER2/CEP17 ratio of 3.0, consistent with HER2-positive disease. Given the new diagnosis of HER2-positive metastases, the woman began treatment with docetaxel, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab. (f) Maximum intensity projection image from fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT performed before initiation of therapy and (g) after 2 months of therapy demonstrate a substantial partial response (arrows in f and g indicate hepatic [standardized uptake value, 4.5 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] and osseous [standardized uptake value, 8.4 before therapy, standardized uptake value equal to background after therapy] reference lesions).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/86e3/7543717/097b30c1ea6c/radiol.2020192828.fig1g.gif)

Comment in
-
PET Molecular Imaging as a Tool for Precision Oncology.Radiology. 2020 Aug;296(2):379-380. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020201969. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Radiology. 2020. PMID: 32519934 No abstract available.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987;235(4785):177–182. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, et al. . Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 2001;344(11):783–792. - PubMed
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, et al. . Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2005;353(16):1673–1684. - PubMed
-
- McGranahan N, Swanton C. Biological and therapeutic impact of intratumor heterogeneity in cancer evolution. Cancer Cell 2015;27(1):15–26 [Published correction appears in Cancer Cell 2015;28(1):141.]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

