Fifteen Years of Wireless Sensors for Balance Assessment in Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 32517315
- PMCID: PMC7308812
- DOI: 10.3390/s20113247
Fifteen Years of Wireless Sensors for Balance Assessment in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
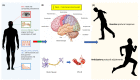
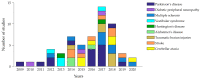
Balance impairment is a major mechanism behind falling along with environmental hazards. Under physiological conditions, ageing leads to a progressive decline in balance control per se. Moreover, various neurological disorders further increase the risk of falls by deteriorating specific nervous system functions contributing to balance. Over the last 15 years, significant advancements in technology have provided wearable solutions for balance evaluation and the management of postural instability in patients with neurological disorders. This narrative review aims to address the topic of balance and wireless sensors in several neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and other neurodegenerative and acute clinical syndromes. The review discusses the physiological and pathophysiological bases of balance in neurological disorders as well as the traditional and innovative instruments currently available for balance assessment. The technical and clinical perspectives of wearable technologies, as well as current challenges in the field of teleneurology, are also examined.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; balance; cerebellar ataxia; multiple sclerosis; posturography; stroke; vestibular syndrome; wearables; wireless sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ageing and Health. [(accessed on 16 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
-
- World Health Organization, editor. WHO Global Report on Falls Prevention in Older Age. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

