Moving Forward with Dysphagia Care: Implementing Strategies during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond
- PMID: 32519150
- PMCID: PMC7282541
- DOI: 10.1007/s00455-020-10144-9
Moving Forward with Dysphagia Care: Implementing Strategies during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond
Abstract
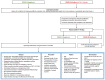
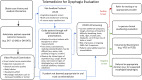
Growing numbers of SARS-CoV-2 cases coupled with limited understanding of transmissibility and virulence, have challenged the current workflow and clinical care pathways for the dysphagia provider. At the same time, the need for non-COVID-19-related dysphagia care persists. Increased awareness of asymptomatic virus carriers and variable expression of the disease have also focused attention to appropriate patient care in the context of protection for the healthcare workforce. The objective of this review was to create a clinical algorithm and reference for dysphagia clinicians across clinical settings to minimize spread of COVID-19 cases while providing optimal care to patients suffering from swallowing disorders. Every practitioner and healthcare system will likely have different constraints or preferences leading to the utilization of one technique over another. Knowledge about this pandemic increases every day, but the algorithms provided here will help in considering the best options for proceeding with safe and effective dysphagia care in this new era.
Keywords: Assessment; COVID-19; Dysphagia; SARS-CoV-2; Telemedicine; Treatment.
Figures

References
-
- Johns Hopkins University and Medicine. Coronavirus Resource Center. 2020; https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. Accessed June 5, 2020.
-
- Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, Barnaby DP, Becker LB, Chelico JD, Cohen SL, Cookingham J, Coppa K, Diefenbach MA, Dominello AJ, Duer-Hefele J, Falzon L, Gitlin J, Hajizadeh N, Harvin TG, Hirschwerk DA, Kim EJ, Kozel ZM, Marrast LM, Mogavero JN, Osorio GA, Qiu M, Zanos TP. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6775. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Helms J, Tacquard C, Severac F, Leonard-Lorant I, Ohana M, Delabranche X, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R, Schenck M, Fagot Gandet F, Fafi-Kremer S, Castelain V, Schneider F, Grunebaum L, Angles-Cano E, Sattler L, Mertes PM, Meziani F. High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06062-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

