Acute and Sub-Acute Toxicological Evaluations of Bioactive Alkaloidal Extract from Melodinus henryi and Their Main Chemical Constituents
- PMID: 32519306
- PMCID: PMC7367981
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-020-00252-2
Acute and Sub-Acute Toxicological Evaluations of Bioactive Alkaloidal Extract from Melodinus henryi and Their Main Chemical Constituents
Abstract
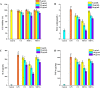
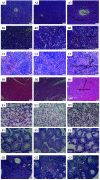
Melodinus henryi is a good source of terpenoid indole alkaloids, and traditionally used as a folk medicine in the treatment of meningitis and fracture. In order to further exploit their potential uses, its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activities, safety evaluations and chemical profiles have been illustrated. Compared to the crude methanol extract from M. henryi and its non-alkaloidal fraction, the total alkaloidal fraction (MHTA) had the strongest anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activities. In the acute oral toxicity assay, the half lethal dose (LD50) of MHTA was more than 2000 mg/kg. The sub-acute toxicity assay for consecutive 28 days exhibited MHTA at a lower concentrations of less than 500 mg/kg might be regarded as safe, and might damage spleen, liver, kidney, and heart when the dose is higher than 1000 mg/kg. In addition, a phytochemical investigation on MHTA led to the isolation of 15 monoterpenoid indole alkaloids. Thus, in regard with the potent side effects of MHTA, it should be used with caution in the development of phytomedicine.
Keywords: Acute toxicity; Melodinus henryi; Monoterpenoid indole alkaloids; Subacute toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Melohenines A and B, two unprecedented alkaloids from Melodinus henryi.Org Lett. 2009 Nov 5;11(21):4834-7. doi: 10.1021/ol9018826. Org Lett. 2009. PMID: 19863145
-
Monoterpenoid indole alkaloids from the bark of Melodinus henryi.Fitoterapia. 2019 Oct;138:104354. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104354. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Fitoterapia. 2019. PMID: 31473334
-
Six new alkaloids from Melodinus henryi.Fitoterapia. 2015 Jan;100:133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2014.11.021. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Fitoterapia. 2015. PMID: 25481371
-
Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don: A review of its ethnobotany, phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology and toxicities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;284:114647. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114647. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34562562 Review.
-
[Chemical studies of indole alkaloids].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1995 May;115(5):351-69. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.115.5_351. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1995. PMID: 7595863 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Akuammiline alkaloid derivatives: divergent synthesis and effect on the proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Front Chem. 2023 Apr 28;11:1179948. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1179948. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37188095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choudhary GP, Jain AP. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2016;7:175–184.
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. J. Nat. Prod. 2016;79:629–661. - PubMed
-
- Bharate SS, Serge M, Vishwakarma RA. J. Med. Chem. 2018;61:10345–10374. - PubMed
-
- Khalifa SA, De Medina P, Erlandsson A, El-Seedi HR, Silvente-Poirot S, Poirot M. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2014;446:681–686. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

