Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Arenes and Heteroarenes
- PMID: 32519788
- PMCID: PMC7702167
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202002777
Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Arenes and Heteroarenes
Abstract
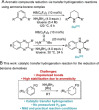
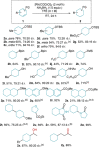
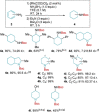
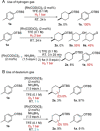
Transfer hydrogenation reactions are of great interest to reduce diverse molecules under mild reaction conditions. To date, this type of reaction has only been successfully applied to alkenes, alkynes and polarized unsaturated compounds such as ketones, imines, pyridines, etc. The reduction of benzene derivatives by transfer hydrogenation has never been described, which is likely due to the high energy barrier required to dearomatize these compounds. In this context, we have developed a catalytic transfer hydrogenation reaction for the reduction of benzene derivatives and heteroarenes to form complex 3-dimensional scaffolds bearing various functional groups at room temperature without needing compressed hydrogen gas.
Keywords: arene reduction; catalysis; organic chemistry; rhodium; transfer hydrogenation.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang D., Astruc D., Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6621–6686. - PubMed
-
- Baráth E., Catalysts 2018, 8, 671–695.
-
- Knoevenagel E., Bergdolt B., Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1903, 36, 2857–2860.
-
- For the transfer hydrogenation reaction of polarized functional groups such as ketones, aldehydes and nitro groups using rhodium nanoparticles see:
-
- Serrano-Maldonado A., Martin E., Guerrero-Ríos I., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2863–2870;
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

