Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis Treated with Interferon-γ and Dupilumab
- PMID: 32521134
- PMCID: PMC7333509
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2000024
Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis Treated with Interferon-γ and Dupilumab
Abstract
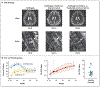
We describe a case of life-threatening disseminated coccidioidomycosis in a previously healthy child. Like most patients with disseminated coccidioidomycosis, this child had no genomic evidence of any known, rare immune disease. However, comprehensive immunologic testing showed exaggerated production of interleukin-4 and reduced production of interferon-γ. Supplementation of antifungal agents with interferon-γ treatment slowed disease progression, and the addition of interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 blockade with dupilumab resulted in rapid resolution of the patient's clinical symptoms. This report shows that blocking of type 2 immune responses can treat infection. This immunomodulatory approach could be used to enhance immune clearance of refractory fungal, mycobacterial, and viral infections. (Supported by the Jeffrey Modell Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.).
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Galgiani JN, Ampel NM, Blair JE, et al. Coccidioidomycosis. Clin Infect Dis 2005;41:1217–23. - PubMed
-
- Dewsnup DH, Galgiani JN, Graybill JR, et al. Is it ever safe to stop azole therapy for Coccidioides immitis meningitis? Ann Intern Med 1996;124:305–10. - PubMed
-
- Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ. Epidemiology of invasive mycoses in North America. Crit Rev MicrobioI 2010;36:1–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
