Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Oncology: An Update
- PMID: 32521645
- PMCID: PMC7352852
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12061493
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Oncology: An Update
Abstract
To date, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is included in routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols for several cancers. The real additive role of DWI lies in the "functional" information obtained by probing the free diffusivity of water molecules into intra and inter-cellular spaces that in tumors mainly depend on cellularity. Although DWI has not gained much space in some oncologic scenarios, this non-invasive tool is routinely used in clinical practice and still remains a hot research topic: it has been tested in almost all cancers to differentiate malignant from benign lesions, to distinguish different malignant histotypes or tumor grades, to predict and/or assess treatment responses, and to identify residual or recurrent tumors in follow-up examinations. In this review, we provide an up-to-date overview on the application of DWI in oncology.
Keywords: apparent diffusion coefficient; cancer imaging; diffusion weighted imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; oncologic imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

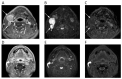
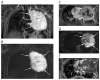
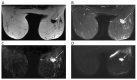
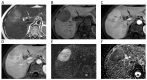
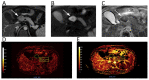
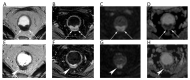

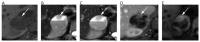
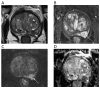
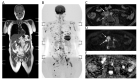
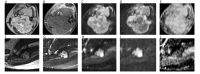
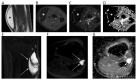
References
-
- Svolos P., Kousi E., Kapsalaki E., Theodorou K., Fezoulidis I., Kappas C., Tsougos I. The role of diffusion and perfusion weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of cerebral tumors: A review and future perspectives Tumour charcterisation. Cancer Imaging. 2014;14:20. doi: 10.1186/1470-7330-14-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muccio C.F., Caranci F., D’Arco F., Cerase A., De Lipsis L., Esposito G., Tedeschi E., Andreula C. Magnetic resonance features of pyogenic brain abscesses and differential diagnosis using morphological and functional imaging studies: A pictorial essay. J. Neuroradiol. 2014;41:153–167. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2014.05.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee E.J., terBrugge K., Mikulis D., Choi D.S., Bae J.M., Lee S.K., Moon S.Y. Diagnostic value of peritumoral minimum apparent diffusion coefficient for differentiation of glioblastoma multiforme from solitary metastatic lesions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011;196:71–76. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.4752. - DOI - PubMed

