p53-PHLDA3-Akt Network: The Key Regulators of Neuroendocrine Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 32521808
- PMCID: PMC7312810
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21114098
p53-PHLDA3-Akt Network: The Key Regulators of Neuroendocrine Tumorigenesis
Abstract
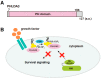
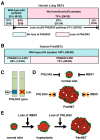
p53 is a well-known tumor suppressor gene and one of the most extensively studied genes in cancer research. p53 functions largely as a transcription factor and can trigger a variety of antiproliferative programs via induction of its target genes. We identified PHLDA3 as a p53 target gene and found that its protein product is a suppressor of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) and a repressor of Akt function. PHLDA3 is frequently inactivated by loss of heterozygosity (LOH) and methylation in human PanNETs, and LOH at the PHLDA3 gene locus correlates with PanNET progression and poor prognosis. In addition, in PHLDA3-deficient mice, pancreatic islet cells proliferate abnormally and acquire resistance to apoptosis. In this article, we briefly review the roles of p53 and Akt in human neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) and describe the relationship between the p53-PHLDA3 and Akt pathways. We also discuss the role of PHLDA3 as a tumor suppressor in various NETs and speculate on the possibility that loss of PHLDA3 function may be a useful prognostic marker for NET patients indicating particular drug therapies. These results suggest that targeting the downstream PHLDA3-Akt pathway might provide new therapies to treat NETs.
Keywords: Akt; PHLDA3; neuroendocrine tumor; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Hainaut P., Hollstein M. P53 and human cancer: The first ten thousand mutations. Adv. Cancer Res. 2000;77:81–137. - PubMed
-
- Greenblatt M., Bennett W.P., Hollstein M., Harris C. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994;54:4855–4878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 17H03587/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 20K07605/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 19K16732/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 18F18758/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 27th Pancreatic Disease Research Award/Pancreas Research Foundation of Japan
- Collaborative Research Grant/Cancer Research Institute of Kanazawa University
- Scholarship Grant for Living Expenses of Foreign Nationals in Japan/Ichiro Kanehara Foundation for the Promotion of Medical Sciences and Medical Care
- Applied Research for Innovative Treatment of Cancer from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- Project for Development of Innovative Research on Cancer Therapeutics (P-Direct)/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- Project for Cancer Research and Therapeutic Evolution (P-Create)/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- Research Grant of the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund/Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund
- the Mitsubishi Foundation/Mitsubishi Foundation
- the NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan) for the Promotion of Science/NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan) for the Promotion of Science
- the Project Mirai Cancer Research Grants/the Project Mirai Cancer Research Grants
- the Okinaka Memorial Institute for Medical Research/Okinaka Memorial Institute for Medical Research
- the Life Science Foundation of Japan/Life Science Foundation of Japan
- Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research in Japan/Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

