Prognostic value of lymph node to primary tumor standardized uptake value ratio in unresectable esophageal cancer
- PMID: 32522275
- PMCID: PMC7288503
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07044-4
Prognostic value of lymph node to primary tumor standardized uptake value ratio in unresectable esophageal cancer
Abstract
Background: Unresectable esophageal cancer harbors high mortality despite chemoradiotherapy. Better patient selection for more personalized management may result in better treatment outcomes. We presume the ratio of maximum standardized uptake value (SUV) of metastatic lymph nodes to primary tumor (NTR) in 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) may provide prognostic information and further stratification of these patients.
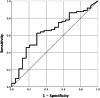
Methods: The patients with non-metastatic and unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) receiving FDG PET/CT staging and treated by chemoradiotherapy were retrospectively reviewed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to determine the optimal cut-off value for NTR. Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression model were used for survival analyses and multivariable analyses, respectively.
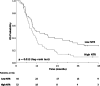
Results: From 2010 to 2016, 96 eligible patients were analyzed. The median follow-up time was 10.2 months (range 1.6 to 83.6 months). Using ROC analysis, the best NTR cut-off value was 0.46 for prediction of distant metastasis. The median distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) was significantly lower in the high-NTR group (9.5 vs. 22.2 months, p = 0.002) and median overall survival (OS) (9.5 vs. 11.6 months, p = 0.013) was also significantly worse. Multivariable analysis revealed that NTR was an independent prognostic factor for DMFS (hazard ratio [HR] 1.81, p = 0.023) and OS (HR 1.77, p = 0.014).
Conclusions: High pretreatment NTR predicts worse treatment outcomes and could be an easy-to-use and helpful prognostic factor to provide more personalized treatment for patients with non-metastatic and unresectable esophageal SCC.
Keywords: 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET); Distant metastasis; Esophageal cancer; Maximum standardized uptake value (SUV); Node-to-tumor SUV ratio (NTR); Personalized treatment; Prognosis; Ratio; Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC); Unresectable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic parameters of sequential 18F-FDG PET/CT predict overall survival of esophageal cancer patients treated with (chemo-) radiation.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Feb 19;14(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1236-x. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30782182 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of nodal maximum standardized uptake value of pretreatment [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging in patients with esophageal cancer.Dis Esophagus. 2017 Aug 1;30(8):1-10. doi: 10.1093/dote/dox021. Dis Esophagus. 2017. PMID: 28575243
-
Confirmation of the prognostic value of pretherapeutic tumor SUR and MTV in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Jul;46(7):1485-1494. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04307-6. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30949816
-
Utility of PET, CT, and EUS to identify pathologic responders in esophageal cancer.Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Oct;78(4):1152-60; discussion 1152-60. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.04.046. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15464463 Review.
-
Prognostic and predictive values of interim 18F-FDG PET during neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Nucl Med. 2021 Apr;35(4):447-457. doi: 10.1007/s12149-021-01583-x. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Ann Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 33471289
Cited by
-
The prognostic value of lymph node to primary tumor standardized uptake value ratio in cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Ann Nucl Med. 2024 Aug;38(8):607-618. doi: 10.1007/s12149-024-01933-5. Epub 2024 May 9. Ann Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 38724805
-
Could tumour volume and major and minor axis based on CTA statistical anatomy improve the pre-operative T-stage in oesophageal cancer?Cancer Med. 2023 Jul;12(13):14037-14051. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6051. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37306615 Free PMC article.
-
Is CT Radiomics Superior to Morphological Evaluation for pN0 Characterization? A Pilot Study in Colon Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;16(3):660. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030660. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339411 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of pretreatment [18F]FDG PET/CT parameters in esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun;35(6):3396-3408. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11207-3. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39570366
-
Prognostic Utility of Neck Lymph Node-to-Primary Tumor Standardized Uptake Value Ratio in Oral Cavity Cancer.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 11;11(7):1954. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071954. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamaguchi S, Morita M, Yamamoto M, Egashira A, Kawano H, Kinjo N, et al. Long-term outcome of definitive Chemoradiotherapy and induction Chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for T4 esophageal Cancer with tracheobronchial invasion. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(11):3280–3287. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6656-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

