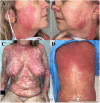
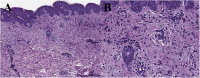
Hydroxychloroquine-induced erythema multiforme in a patient with COVID-19
- PMID: 32522372
- PMCID: PMC7236751
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.05.004
Hydroxychloroquine-induced erythema multiforme in a patient with COVID-19
Similar articles
-
Erythema multiforme in the context of SARS-Coronavirus-2 infection.Med Clin (Barc). 2020 Aug 14;155(3):141. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.04.016. Epub 2020 May 8. Med Clin (Barc). 2020. PMID: 32475615 Free PMC article. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19: How to use it waiting for conclusive scientific evidence.Med Clin (Barc). 2020 Aug 14;155(3):134-135. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.05.006. Epub 2020 May 16. Med Clin (Barc). 2020. PMID: 32425245 Free PMC article. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in covid-19.BMJ. 2020 Apr 8;369:m1432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1432. BMJ. 2020. PMID: 32269046 No abstract available.
-
Safety considerations with chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in the management of SARS-CoV-2 infection.CMAJ. 2020 Apr 27;192(17):E450-E453. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.200528. Epub 2020 Apr 8. CMAJ. 2020. PMID: 32269021 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Of chloroquine and COVID-19.Antiviral Res. 2020 May;177:104762. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104762. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32147496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral mechanisms of candidate chemical medicines and traditional Chinese medicines for SARS-CoV-2 infection.Virus Res. 2020 Sep;286:198073. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198073. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32592817 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources