Serum neurofilament light chain levels are associated with white matter integrity in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 32522711
- PMCID: PMC7363568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104960
Serum neurofilament light chain levels are associated with white matter integrity in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
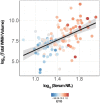
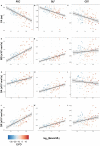
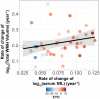
Neurofilament light chain (NfL) is a protein that is selectively expressed in neurons. Increased levels of NfL measured in either cerebrospinal fluid or blood is thought to be a biomarker of neuronal damage in neurodegenerative diseases. However, there have been limited investigations relating NfL to the concurrent measures of white matter (WM) decline that it should reflect. White matter damage is a common feature of Alzheimer's disease. We hypothesized that serum levels of NfL would associate with WM lesion volume and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics cross-sectionally in 117 autosomal dominant mutation carriers (MC) compared to 84 non-carrier (NC) familial controls as well as in a subset (N = 41) of MC with longitudinal NfL and MRI data. In MC, elevated cross-sectional NfL was positively associated with WM hyperintensity lesion volume, mean diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and axial diffusivity and negatively with fractional anisotropy. Greater change in NfL levels in MC was associated with larger changes in fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and radial diffusivity, all indicative of reduced WM integrity. There were no relationships with NfL in NC. Our results demonstrate that blood-based NfL levels reflect WM integrity and supports the view that blood levels of NfL are predictive of WM damage in the brain. This is a critical result in improving the interpretability of NfL as a marker of brain integrity, and for validating this emerging biomarker for future use in clinical and research settings across multiple neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Blood-based biomarkers; Neurodegeneration; Neurofilament; Neuroimaging; White matter.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest A.M.G. has consulted for Cognition Therapeutics, Biogen, GSK, Illumina, Eisai, AbbVie and Pfizer and served on the SAB for Denali Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Araque Caballero M.Á., Suárez-Calvet M., Duering M., Franzmeier N., Benzinger T., Fagan A.M., Bateman R.J., Jack C.R., Levin J., Dichgans M., Jucker M., Karch C., Masters C.L., Morris J.C., Weiner M., Rossor M., Fox N.C., Lee J.-H., Salloway S., Danek A., Goate A., Yakushev I., Hassenstab J., Schofield P.R., Haass C., Ewers M. White matter diffusion alterations precede symptom onset in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2018;141:3065–3080. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barry D.M., Stevenson W., Bober B.G., Wiese P.J., Dale J.M., Barry G.S., Byers N.S., Strope J.D., Chang R., Schulz D.J., Shah S., Calcutt N.A., Gebremichael Y., Garcia M.L. Expansion of neurofilament medium C terminus increases axonal diameter independent of increases in conduction velocity or myelin thickness. J. Neurosci. 2012;32:6209–6219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0647-12.2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bateman R.J., Xiong C., Benzinger T.L.S., Fagan A.M., Goate A., Fox N.C., Marcus D.S., Cairns N.J., Xie X., Blazey T.M., Holtzman D.M., Santacruz A., Buckles V., Oliver A., Moulder K., Aisen P.S., Ghetti B., Klunk W.E., McDade E., Martins R.N., Masters C.L., Mayeux R., Ringman J.M., Rossor M.N., Schofield P.R., Sperling, R. a, Salloway, S., Morris, J.C. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:795–804. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1202753. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benzinger T.L.S., Blazey T., Jack C.R., Koeppe R.A., Su Y., Xiong C., Raichle M.E., Snyder A.Z., Ances B.M., Bateman R.J., Cairns N.J., Fagan A.M., Goate A., Marcus D.S., Aisen P.S., Christensen J.J., Ercole L., Hornbeck R.C., Farrar A.M., Aldea P., Jasielec M.S., Owen C.J., Xie X., Mayeux R., Brickman A., McDade E., Klunk W., Mathis C.A., Ringman J., Thompson P.M., Ghetti B., Saykin A.J., Sperling R.A., Johnson K.A., Salloway S., Correia S., Schofield P.R., Masters C.L., Rowe C., Villemagne V.L., Martins R., Ourselin S., Rossor M.N., Fox N.C., Cash D.M., Weiner M.W., Holtzman D.M., Buckles V.D., Moulder K., Morris J.C. Regional variability of imaging biomarkers in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013;110:E4502–E4509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317918110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bridel C., Van Wieringen W.N., Zetterberg H., Tijms B.M., Teunissen C.E., Alvarez-Cermeño J.C., Andreasson U., Axelsson M., Bäckström D.C., Bartos A., Bjerke M., Blennow K., Boxer A., Brundin L., Burman J., Christensen T., Fialová L., Forsgren L., Frederiksen J.L., Gisslén M., Gray E., Gunnarsson M., Hall S., Hansson O., Herbert M.K., Jakobsson J., Jessen-Krut J., Janelidze S., Johannsson G., Jonsson M., Kappos L., Khademi M., Khalil M., Kuhle J., Landén M., Leinonen V., Logroscino G., Lu C.H., Lycke J., Magdalinou N.K., Malaspina A., Mattsson N., Meeter L.H., Mehta S.R., Modvig S., Olsson T., Paterson R.W., Pérez-Santiago J., Piehl F., Pijnenburg Y.A.L., Pyykkö O.T., Ragnarsson O., Rojas J.C., Romme Christensen J., Sandberg L., Scherling C.S., Schott J.M., Sellebjerg F.T., Simone I.L., Skillbäck T., Stilund M., Sundström P., Svenningsson A., Tortelli R., Tortorella C., Trentini A., Troiano M., Turner M.R., Van Swieten J.C., Vågberg M., Verbeek M.M., Villar L.M., Visser P.J., Wallin A., Weiss A., Wikkelsø C., Wild E.J. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light protein in neurology: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019 doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.1534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

