ACE2 and COVID-19 and the resulting ARDS
- PMID: 32522846
- PMCID: PMC10016912
- DOI: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137935
ACE2 and COVID-19 and the resulting ARDS
Abstract
This article reviews the correlation between ACE2 and COVID-19 and the resulting acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). ACE2 is a crucial component of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). The classical ACE-angiotensin Ⅱ (Ang II)-angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT1R) axis and the ACE2-Ang(1-7)-Mas counter-regulatory axis play an essential role in RAS system. ACE2 antagonises the activation of the classical RAS ACE-Ang II-AT1R axis and protects against lung injury. Similar to severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) also uses ACE2 for cell entry. ARDS is a clinical high-mortality disease which is probably due to the excessive activation of RAS caused by 2019-nCoV infection, and ACE2 has a protective effect on ARDS caused by COVID-19. Because of these protective effects of ACE2 on ARDS, the development of drugs enhancing ACE2 activity may become one of the most promising approaches for the treatment of COVID-19 in the near future. In the meantime, however, the use of RAS blockers such as ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers that inhibit the damaging (ACE-Ang II) arm of the RAS cascade in the lung may also be promising. Trial registration number: NCT04287686.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
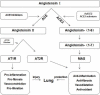
Similar articles
-
Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19.J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):726-730. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25785. Epub 2020 Apr 5. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32221983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):L325-L336. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00189.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32639866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two hits to the renin-angiotensin system may play a key role in severe COVID-19.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Jun;36(6):389-392. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12237. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32492292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19.Rev Med Virol. 2020 Sep;30(5):e2119. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2119. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32584474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers and the COVID-19 Pandemic: At Present There Is No Evidence to Abandon Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers.Hypertension. 2020 Jun;75(6):1382-1385. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15082. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32208987 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Evaluation of Drugs as Potential Modulators of the Trafficking and Maturation of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 27;14(7):764. doi: 10.3390/biom14070764. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062478 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity of CD200/CD200R pathway in LPS-induced lung inflammation.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;13:1092126. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1092126. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591265 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine, Qingfei Paidu Decoction and Xuanfei Baidu Decoction, Inhibited Cytokine Production via NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Macrophages: Implications for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 26;12:722126. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.722126. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34764867 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-COV-2/COVID-19: scenario, epidemiology, adaptive mutations, and environmental factors.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Oct;29(46):69117-69136. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-22333-0. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35947257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Pathogenesis: From Molecular Pathway to Vaccine Administration.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 27;9(8):903. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080903. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440107 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organisation . Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected-Interim guidance. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus
-
- World Health Organisation . WHO Director-General’sremarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. Available: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

