Multidisciplinary care in Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- PMID: 32523661
- PMCID: PMC7236394
- DOI: 10.1177/2040622319894469
Multidisciplinary care in Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Abstract
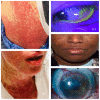
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) are potentially fatal mucocutaneous diseases that can involve many organ systems. Manifestations of SJS/TEN outside of the skin, eyes, and oral mucosa are not well defined or well recognized, and, therefore, are often not addressed clinically. As supportive care improves and mortality from SJS/TEN decreases, chronic complications in affected organ systems are becoming more prevalent. Recognition of the manifestations of SJS/TEN in the acute phase is critical to optimal care. In this review, we review the organ systems that may be involved in SJS/TEN, provide an overview of their management, and propose a list of items that should be communicated to the patient and family upon discharge. The organ systems discussed include the pulmonary, gastrointestinal/hepatic, oral, otorhinolaryngologic, gynecologic, genitourinary, and renal systems. In addition, the significant psychosocial, nutritional, and pain consequences and management of SJS/TEN are discussed.
Keywords: Stevens-Johnson syndrome; burns; complications; gastrointestinal; gynecologic; ocular; pulmonary; toxic epidermal necrolysis.
© The Author(s), 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, et al. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol 1993; 129: 92–96. - PubMed
-
- Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Eng J Med 1995; 333: 1600–1607. - PubMed
-
- Sassolas B, Haddad C, Mockenhaupt M, et al. ALDEN, an algorithm for assessment of drug causality in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: comparison with case-control analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2010; 88: 60–68. - PubMed
-
- Kohanim S, Palioura S, Saeed HN, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis–a comprehensive review and guide to therapy. I. systemic disease. Ocul Surf 2016; 14: 2–19. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

