Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates carry mutational signatures of host immune environments
- PMID: 32524000
- PMCID: PMC7259932
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba4901
Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates carry mutational signatures of host immune environments
Abstract
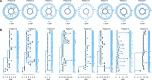
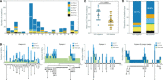
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection results in a spectrum of clinical and histopathologic manifestations. It has been proposed that the environmental and immune pressures associated with different contexts of infection have different consequences for the associated bacterial populations, affecting drug susceptibility and the emergence of resistance. However, there is little concrete evidence for this model. We prospectively collected sputum samples from 18 newly diagnosed and treatment-naïve patients with tuberculosis and sequenced 795 colony-derived Mtb isolates. Mutant accumulation rates varied considerably between different bacilli isolated from the same individual, and where high rates of mutation were observed, the mutational spectrum was consistent with reactive oxygen species-induced mutagenesis. Elevated bacterial mutation rates were identified in isolates from HIV-negative but not HIV-positive individuals, suggesting that they were immune-driven. These results support the model that mutagenesis of Mtb in vivo is modulated by the host environment, which could drive the emergence of variants associated with drug resistance in a host-dependent manner.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

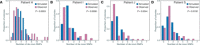
References
-
- McGrath M., Gey van Pittius N. C., van Helden P. D., Warren R. M., Warner D. F., Mutation rate and the emergence of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69, 292–302 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Ford C. B., Shah R. R., Maeda M. K., Gagneux S., Murray M. B., Cohen T., Johnston J. C., Gardy J., Lipsitch M., Fortune S. M., Mycobacterium tuberculosis mutation rate estimates from different lineages predict substantial differences in the emergence of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Nat. Genet. 45, 784–790 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

