Sleep disruption is not observed with brain-responsive neurostimulation for epilepsy
- PMID: 32524041
- PMCID: PMC7278540
- DOI: 10.1002/epi4.12382
Sleep disruption is not observed with brain-responsive neurostimulation for epilepsy
Abstract
Objective: Neurostimulation devices that deliver electrical impulses to the nervous system are widely used to treat seizures in patients with medically refractory epilepsy, but the effects of these therapies on sleep are incompletely understood. Vagus nerve stimulation can contribute to obstructive sleep apnea, and thalamic deep brain stimulation can cause sleep disruption. A device for brain-responsive neurostimulation (RNS® System, NeuroPace, Inc) is well tolerated in clinical trials, but potential effects on sleep are unknown.
Methods: Six adults with medically refractory focal epilepsy treated for at least six months with the RNS System underwent a single night of polysomnography (PSG). RNS System lead locations included mesial temporal and neocortical targets. Sleep stages and arousals were scored according to standard guidelines. Stimulations delivered by the RNS System in response to detections of epileptiform activity were identified by artifacts on scalp electroencephalography.
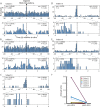
Results: One subject was excluded for technical reasons related to unreliable identification of stimulation artifact on EEG during PSG. In the remaining five subjects, PSG showed fragmented sleep with frequent arousals. Arousal histograms aligned to stimulations revealed a significant peak in arousals just before stimulation. In one of these subjects, the arousal peak began before stimulation and extended ~1 seconds after stimulation. A peak in arousals occurring only after stimulation was not observed.
Significance: In this small cohort of patients, brain-responsive neurostimulation does not appear to disrupt sleep. If confirmed in larger studies, this could represent a potential clinical advantage of brain-responsive neurostimulation over other neurostimulation modalities.
Keywords: RNS; arousal; brain‐responsive neurostimulation; epilepsy; polysomnography; sleep.
© 2020 The Authors. Epilepsia Open published by Wiley Periodicals Inc. on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
BJ and TKT are employees of, and hold stock options at, NeuroPace, Inc. VRR is a paid consultant for NeuroPace, Inc, but does not have equity or ownership in the company. Other authors declare no relevant conflicts of interest. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures



References
-
- Markert MS, Fisher RS. Neuromodulation ‐ science and practice in epilepsy: vagus nerve stimulation, thalamic deep brain stimulation, and responsive neurostimulation. Expert Rev Neurother. 2019;19:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Benbadis SR, Geller E, Ryvlin P, Schachter S, Wheless J, Doyle W, et al. Putting it all together: options for intractable epilepsy: an updated algorithm on the use of epilepsy surgery and neurostimulation. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;88S:33–8. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RS, Velasco AL. Electrical brain stimulation for epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10:261–70. - PubMed

