Radiomics in Breast Imaging from Techniques to Clinical Applications: A Review
- PMID: 32524780
- PMCID: PMC7289696
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0855
Radiomics in Breast Imaging from Techniques to Clinical Applications: A Review
Abstract
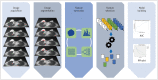
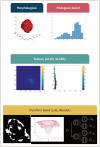
Recent advances in computer technology have generated a new area of research known as radiomics. Radiomics is defined as the high throughput extraction and analysis of quantitative features from imaging data. Radiomic features provide information on the gray-scale patterns, inter-pixel relationships, as well as shape and spectral properties of radiological images. Moreover, these features can be used to develop computational models that may serve as a tool for personalized diagnosis and treatment guidance. Although radiomics is becoming popular and widely used in oncology, many problems such as overfitting and reproducibility issues remain unresolved. In this review, we will outline the steps of radiomics used for oncology, specifically addressing applications for breast cancer patients and focusing on technical issues.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Informatics; Quantitative imaging; Radiomics; Texture.
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiomics: a new application from established techniques.Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev. 2016;1(2):207-226. doi: 10.1080/23808993.2016.1164013. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Expert Rev Precis Med Drug Dev. 2016. PMID: 28042608 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric radiomics methods for breast cancer tissue characterization using radiological imaging.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Apr;180(2):407-421. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05533-5. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32020435 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of radiomics in breast cancer diagnosis and prognostication.Breast. 2020 Feb;49:74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.10.018. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Breast. 2020. PMID: 31739125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomics in breast MRI: current progress toward clinical application in the era of artificial intelligence.Radiol Med. 2022 Jan;127(1):39-56. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01423-y. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Radiol Med. 2022. PMID: 34704213 Review.
-
Radiomics in breast cancer: Current advances and future directions.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Sep 17;5(9):101719. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101719. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39293402 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differentiating Glioblastoma Multiforme from Brain Metastases Using Multidimensional Radiomics Features Derived from MRI and Multiple Machine Learning Models.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 28;2022:2016006. doi: 10.1155/2022/2016006. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36212721 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics and Machine Learning with Multiparametric Breast MRI for Improved Diagnostic Accuracy in Breast Cancer Diagnosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 May 21;11(6):919. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11060919. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063774 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based diagnostic evaluation of shear-wave elastography in BI-RADS category 4 breast cancer screening: a multicenter, retrospective study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Feb;12(2):1223-1234. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-341. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35111618 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction Breast Molecular Typing of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Based on Dynamic Contrast Enhancement Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics Characteristics: A Feasibility Study.Front Oncol. 2022 May 19;12:799232. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.799232. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35664741 Free PMC article.
-
Vascularity and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Front Radiol. 2021 Dec 9;1:735567. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2021.735567. eCollection 2021. Front Radiol. 2021. PMID: 37492179 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Limkin EJ, Sun R, Dercle L, Zacharaki EI, Robert C, Reuzé S, et al. Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:1191–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical