The Determining Role of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 32524823
- PMCID: PMC7885901
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2019.7929
The Determining Role of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
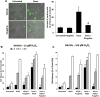
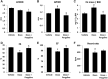
Aims: Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy is a lethal pathology characterized by oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and contractile impairment, leading to cell death. Although extensive research has been done to understand the pathophysiology of doxorubicin cardiomyopathy, no effective treatments are available. We investigated whether monoamine oxidases (MAOs) could be involved in doxorubicin-derived oxidative stress, and in the consequent mitochondrial, cardiomyocyte, and cardiac dysfunction. Results: We used neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) and adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs). Doxorubicin alone (i.e., 0.5 μM doxorubicin) or in combination with H2O2 induced an increase in mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which was prevented by the pharmacological inhibition of MAOs in both NRVMs and AMVMs. The pharmacological approach was supported by the genetic ablation of MAO-A in NRVMs. In addition, doxorubicin-derived ROS caused lipid peroxidation and alterations in mitochondrial function (i.e., mitochondrial membrane potential, permeability transition, redox potential), mitochondrial morphology (i.e., mitochondrial distribution and perimeter), sarcomere organization, intracellular [Ca2+] homeostasis, and eventually cell death. All these dysfunctions were abolished by MAO inhibition. Of note, in vivo MAO inhibition prevented chamber dilation and cardiac dysfunction in doxorubicin-treated mice. Innovation and Conclusion: This study demonstrates that the severe oxidative stress induced by doxorubicin requires the involvement of MAOs, which modulate mitochondrial ROS generation. MAO inhibition provides evidence that mitochondrial ROS formation is causally linked to all disorders caused by doxorubicin in vitro and in vivo. Based upon these results, MAO inhibition represents a novel therapeutic approach for doxorubicin cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; doxorubicin; mitochondria; monoamine oxidase; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Ali MK, Ewer MS, Gibbs HR, Swafford J, and Graff KL. Late doxorubicin-associated cardiotoxicity in children. The possible role of intercurrent viral infection. Cancer 74: 182–188, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Antonucci S, Mulvey JF, Burger N, Di Sante M, Hall AR, Hinchy EC, Caldwell ST, Gruszczyk AV, Deshwal S, Hartley RC, Kaludercic N, Murphy MP, Di Lisa F, and Krieg T. Selective mitochondrial superoxide generation in vivo is cardioprotective through hormesis. Free Radic Biol Med 134: 678–687, 2019 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassani JW, Bassani RA, and Bers DM. Twitch-dependent SR Ca accumulation and release in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol 265: C533–C540, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Belousov VV, Fradkov AF, Lukyanov KA, Staroverov DB, Shakhbazov KS, Terskikh AV, and Lukyanov S. Genetically encoded fluorescent indicator for intracellular hydrogen peroxide. Nat Methods 3: 281–286, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Benard G, Bellance N, James D, Parrone P, Fernandez H, Letellier T, and Rossignol R. Mitochondrial bioenergetics and structural network organization. J Cell Sci 120: 838–848, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

