Atypical Presentation of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 in a Peritoneal Dialysis Patient
- PMID: 32525402
- PMCID: PMC7290252
- DOI: 10.1177/2324709620931238
Atypical Presentation of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 in a Peritoneal Dialysis Patient
Abstract
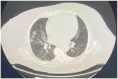
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a rapidly spreading disease causing increased morbidity and mortality across the globe. There is limited available knowledge regarding the natural history of the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Other factors that are also making this infection spread like a pandemic include global travelers, lack of proven treatment, asymptomatic carriers, potential reinfection, underprepared global health care systems, and lack of public awareness and efforts to prevent further spread. It is understood that certain preexisting medical conditions increase the risk of mortality with COVID-19; however, the outcome of this disease in traditionally vulnerable chronic illnesses such as end-stage renal disease is not well documented. We present a case of a 56-year-old African American lady with end-stage renal disease on the peritoneal dialysis who presented predominantly with nausea, vomiting, and subsequently found to have COVID-19. We use this case to illustrate an atypical presentation of the COVID-19 in a vulnerable patient and discuss the literature.
Keywords: COVID-19; atypical presentation; end-stage renal disease; peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Accessed May 16, 2020 https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- Johns Hopkins University. Coronavirus COVID-19 global cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Accessed May 16 2020. https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594...
-
- Ma Y, Diao B, Xifeng LV, et al. 2019. novel coronavirus disease in hemodialysis (HD) patients: report from one HD center in Wuhan, China [published online February 27, 2020]. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.02.24.20027201 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous