Development and initial validation of the Generalized Tracking Questionnaire
- PMID: 32525904
- PMCID: PMC7289427
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234393
Development and initial validation of the Generalized Tracking Questionnaire
Abstract
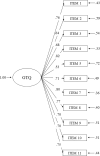
The concept of rule-governed behavior (RGB) has been used in the behavior-analytic literature as a way to analyze complex human behavior, including thinking and problem-solving. Relational frame theory suggests the existence of two main functional types of RGB termed pliance and tracking. In this paper, we describe the development of the Generalized Tracking Questionnaire (GTQ) and the preliminary evaluation of its psychometric properties and validity through three studies, with a total of 1155 participants. In Study 1, a pool of items describing the main characteristics of generalized tracking was designed and evaluated by experts on the RFT account of RGB. The resulting 11 items were administered to 460 undergraduates to examine the understandability and psychometric quality of the items. The exploratory factor analysis indicated that the GTQ can be seen as a unidimensional scale, with all items exhibiting high factor loadings and corrected item-total correlations. In Study 2, the GTQ was administered online to a sample of 464 non-clinical participants and a clinical sample of 125 participants. The one-factor model of the GTQ obtained a good fit in the conducted confirmatory factor analysis. The GTQ showed measurement invariance across gender and clinical and nonclinical participants. It also obtained excellent internal consistency and correlated in theoretically coherent ways with other constructs. In Study 3, the GTQ and a neuropsychological battery of executive functions were administered to 105 participants. The GTQ showed statistically significant, medium-size correlations with working memory tests, verbal fluency, planning, and behavioral inhibition. In conclusion, the GTQ seems to be a promising measure to advance in the empirical analysis of functional classes of RGB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Polish adaptation of the measurements of rule-governed behaviors: Generalized Pliance Questionnaire, Generalized Tracking Questionnaire and Generalized Self-Pliance Questionnaire.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 5;18(4):e0283795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283795. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37018282 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of the Gothenburg Trismus Questionnaire (GTQ).Oral Oncol. 2012 Aug;48(8):730-6. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Oral Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22418239 Free PMC article.
-
Further validation of the Gothenburg Trismus Questionnaire (GTQ).PLoS One. 2020 Dec 17;15(12):e0243805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243805. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33332402 Free PMC article.
-
The Mindful Eating Behavior Scale: Development and Psychometric Properties in a Sample of Dutch Adults Aged 55 Years and Older.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018 Jul;118(7):1277-1290.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Apr 11. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018. PMID: 29655657
-
The Fear of Pain Questionnaire-Short Form (FPQ-SF): factorial validity and psychometric properties.Pain. 2008 Jan;134(1-2):51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.03.033. Epub 2007 May 4. Pain. 2008. PMID: 17482361
Cited by
-
Exploring the relationships between rule-governed behavior and adherence to guidelines aiming to reduce the spread of COVID-19.J Contextual Behav Sci. 2022 Jul;25:73-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2022.06.005. Epub 2022 Jun 17. J Contextual Behav Sci. 2022. PMID: 35756099 Free PMC article.
-
Follow, Flex, and Flout: A Relational Frame Theory Account of Flexibility in the Context of Rule-Governed Behavior.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;15(6):795. doi: 10.3390/bs15060795. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564577 Free PMC article.
-
The Polish adaptation of the measurements of rule-governed behaviors: Generalized Pliance Questionnaire, Generalized Tracking Questionnaire and Generalized Self-Pliance Questionnaire.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 5;18(4):e0283795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283795. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37018282 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of physical fatigue on telephone-based neuropsychological test performance in COVID-19 survivors.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025 Feb;275(1):75-88. doi: 10.1007/s00406-023-01638-2. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 37336825
References
-
- Skinner BF. An operant analysis of problem solving In Kleinmuntz B, editor. Problem solving: research, method and theory. New York: Wiley; 1966. p. 225–257.
-
- Skinner BF. About behaviorism New York: Knopf; 1974.
-
- Vaughan M. Rule-governed behavior in behavior analysis In Hayes S, editor. Rule-Governed Behavior. New York: Plenum Press; 1989. p. 97–118.
-
- Hayes S, Barnes-Holmes D, Wilson K. Contextual behavioral science: Creating a science more adequate to the challenge of the human condition. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science. 2012. December; 1(1–2): p. 1–16. 10.1016/j.jcbs.2012.09.004 - DOI
-
- Luciano C, Valdivia-Salas S, Ruiz F. J. The self as the context for rule-governed behavior In McHugh L, Stewart I, editors. The self and perspective taking: research and applications. Oakland: Context Press; 2012. p. 143–160.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials