Bayesian networks established functional differences between breast cancer subtypes
- PMID: 32525929
- PMCID: PMC7289386
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234752
Bayesian networks established functional differences between breast cancer subtypes
Abstract
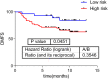
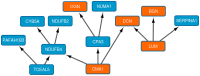
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease. In clinical practice, tumors are classified as hormonal receptor positive, Her2 positive and triple negative tumors. In previous works, our group defined a new hormonal receptor positive subgroup, the TN-like subtype, which had a prognosis and a molecular profile more similar to triple negative tumors. In this study, proteomics and Bayesian networks were used to characterize protein relationships in 96 breast tumor samples. Components obtained by these methods had a clear functional structure. The analysis of these components suggested differences in processes such as mitochondrial function or extracellular matrix between breast cancer subtypes, including our new defined subtype TN-like. In addition, one of the components, mainly related with extracellular matrix processes, had prognostic value in this cohort. Functional approaches allow to build hypotheses about regulatory mechanisms and to establish new relationships among proteins in the breast cancer context.
Conflict of interest statement
JAFV, EE and AG-P are shareholders in Biomedica Molecular Medicine SL, and LT-F, EL-C, AZ-M, and GP-V are currently employees of the company. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
-
- Gámez-Pozo A, Berges-Soria J, Arevalillo JM, Nanni P, López-Vacas R, Navarro H, et al. Combined label-free quantitative proteomics and microRNA expression analysis of breast cancer unravel molecular differences with clinical implications. Cancer Res; 2015. p. 2243–53. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1937 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Waldemarson S, Kurbasic E, Krogh M, Cifani P, Berggård T, Borg Å, et al. Proteomic analysis of breast tumors confirms the mRNA intrinsic molecular subtypes using different classifiers: a large-scale analysis of fresh frozen tissue samples. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18(1):69 Epub 2016/06/29. 10.1186/s13058-016-0732-2 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

