Current status of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for immune/inflammatory lung disorders: Gleaning insights for possible use in COVID-19
- PMID: 32526079
- PMCID: PMC7300965
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.20-0186
Current status of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for immune/inflammatory lung disorders: Gleaning insights for possible use in COVID-19
Abstract
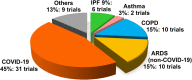
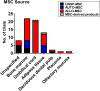
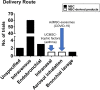
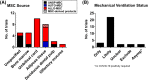
The broad immunomodulatory properties of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have allowed for wide application in regenerative medicine as well as immune/inflammatory diseases, including unmatched allogeneic use. The novel coronavirus disease COVID-19 has unleashed a pandemic in record time accompanied by an alarming mortality rate mainly due to pulmonary injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Because there are no effective preventive or curative therapies currently, MSC therapy (MSCT) has emerged as a possible candidate despite the lack of preclinical data of MSCs for COVID-19. Interestingly, MSCT preclinical data specifically on immune/inflammatory disorders of the lungs were among the earliest to be reported in 2003, with the first clinical use of MSCT for graft-vs-host disease reported in 2004. Since these first reports, preclinical data showing beneficial effects of MSC immunomodulation have accumulated substantially, and as a consequence, over a third of MSCT clinical trials now target immune/inflammatory diseases. There is much preclinical evidence for MSCT in noninfectious-including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-as well as infectious bacterial immune/inflammatory lung disorders, with data generally demonstrating therapeutic effects; however, for infectious viral pulmonary conditions, the preclinical evidence is more scarce with some inconsistent outcomes. In this article, we review the mechanistic evidence for clinical use of MSCs in pulmonary immune/inflammatory disorders, and survey the ongoing clinical trials-including for COVID-19-of MSCT for these diseases, with some perspectives and comment on MSCT for COVID-19.
Keywords: ARDS; COPD; COVID-19; asthma; bacterial pneumonia; clinical trial; cytokine storm; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; influenza; mesenchymal stem cells.
© 2020 The Authors. STEM CELLS TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft‐versus‐host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363:1439‐1441. - PubMed
-
- Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:42‐48. - PubMed
-
- Di Nicola M, Carlo‐Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T‐lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99:3838‐3843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

