Cardiac injuries in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 32526224
- PMCID: PMC7831647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.06.002
Cardiac injuries in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
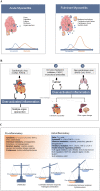
As the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic worsens, this global pandemic is impacting more than 200 countries/regions and more than 4,500,000 confirmed cases worldwide. COVID-19 is caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), which might attack not only the respiratory system, but also the other important organs, including the heart. It was reported that COVID-19 patients with a past history of cardiovascular diseases would have a higher mortality. Meanwhile, elevated troponin levels were frequently observed in COVID-19 cases. Besides the comprehensive treatments for COVID-19, as a cardiologist, we should also remain vigilant about the cardiac injuries, especially those with severe emergent cardiovascular symptoms.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiovascular system; Injury; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.L., Wang X.G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.L., Chen H.D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.D., Liu M.Q., Chen Y., Shen X.R., Wang X., Zheng X.S., Zhao K., Chen Q.J., Deng F., Liu L.L., Yan B., Zhan F.X., Wang Y.Y., Xiao G.F., Shi Z.L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clerkin K.J., Fried J.A., Raikhelkar J., Sayer G., Griffin J.M., Masoumi A., Jain S.S., Burkhoff D., Kumaraiah D., Rabbani L., Schwartz A., Uriel N. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2020;141(20):1648–1655. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow D.L., Finelli L. Preparation for possible sustained transmission of 2019 novel coronavirus: lessons from previous epidemics. JAMA. 2020;323(12):1129–1130. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Kruger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., Muller M.A., Drosten C., Pohlmann S. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271–280.e8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

