Comparing total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty for the treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture in the active elderly over 75 years old: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials
- PMID: 32527294
- PMCID: PMC7291510
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01725-3
Comparing total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty for the treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture in the active elderly over 75 years old: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials
Abstract
Background: Displaced femoral neck fractures (DFNF) are increasingly common in elderly patients. Hip arthroplasty, the recommended treatment of DFNF, consists of the total hip arthroplasty (THA) and hemiarthroplasty (HA). THA is superior to HA in younger patients. However, there are concerns whether the more substantial surgical trauma and higher dislocation rate would trade off the advantages of THA due to frailty and lower physical demands in the elderly over 75 years.
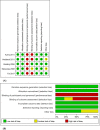
Methods: We conducted the literature search by searching PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Web of Science from the inception dates to June 1, 2019. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Included studies were analyzed according to Cochrane review methods.
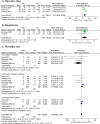
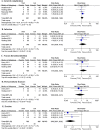
Results: Nine studies met the inclusion criteria totaling 631 participants (301 THA and 330 HA). Four of the studies conducted were identical to a previous study but look at different follow-up periods. Our study revealed that THA was superior in terms of pain HHS, total HHS, EQ-5D, and acetabulum erosion, with a trend of a lower mortality rate within 6 months after surgery. However, the THA group had a longer average operative time and higher dislocation rate, with a trend towards a higher general complication rate. Moreover, there was no significant difference in terms of reoperation rate, postoperative infection, peri-prosthetic fracture, and VTE prevalence across the groups.
Conclusions: THA may be a preferred management option for active elderly patients over 75 years old, which can provide superior hip function and life quality with acceptable risks. Strict management should be followed to prevent dislocation following a THA, especially within the first 6 months.
Trial registration: This study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42019139135).
Keywords: Displaced femoral neck fractures; Hemiarthroplasty; Total hip arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ., 3rd Hip fractures in the elderly: a world-wide projection. Osteoporos Int. 1992;2(6):285–289. - PubMed
-
- Lau EM, Cooper C, Wickham C, Donnan S, Barker DJ. Hip fracture in Hong Kong and Britain. Int J Epidemiol. 1990;19(4):1119–1121. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari M, Swiontkowski M. Management of acute hip fracture. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(21):2053–2062. - PubMed
-
- Parker MJ, Khan RJ, Crawford J, Pryor GA. Hemiarthroplasty versus internal fixation for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly. A randomised trial of 455 patients. J Bone Joint Surg British volume. 2002;84(8):1150–1155. - PubMed
-
- Sonaje JC, Meena PK, Bansiwal RC, Bobade SS. Comparison of functional outcome of bipolar hip arthroplasty and total hip replacement in displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly in a developing country: a 2-year prospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(3):493–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

