A Land of Controversy: Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and Uremic Cardiac Hypertrophy
- PMID: 32527977
- PMCID: PMC7351013
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020010081
A Land of Controversy: Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and Uremic Cardiac Hypertrophy
Abstract
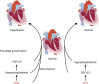
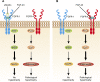
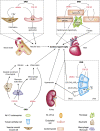
Cardiac hypertrophy is a common feature in patients with CKD. Recent studies revealed that two phosphate regulators, fibroblast growth factor-23 and α-Klotho, are highly involved in the pathophysiologic process of CKD-induced cardiac hypertrophy. With decreasing renal function, elevated fibroblast growth factor-23 and decreased α-Klotho may contribute to cardiac hypertrophy by targeting the heart directly or by inducing systemic changes, such as vascular injury, hemodynamic disorders, and inflammation. However, several studies have demonstrated that disturbances in the fibroblast growth factor-23/α-Klotho axis do not lead to cardiac hypertrophy. In this review, we describe the cardiac effects of the fibroblast growth factor-23/α-Klotho axis and summarize recent progress in this field. In addition, we present not only the main controversies in this field but also provide possible directions to resolve these disputes.
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor-23; uremic cardiac hypertrophy; α-Klotho.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Parfrey PS, Foley RN: The clinical epidemiology of cardiac disease in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 10: 1606–1615, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu I, Minamino T: Physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 97: 245–262, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Shapiro JI: Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of uraemic cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 15: 159–175, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Kato K, Jeanneau C, Tarp MA, Benet-Pagès A, Lorenz-Depiereux B, Bennett EP, et al. .: Polypeptide GalNAc-transferase T3 and familial tumoral calcinosis. Secretion of fibroblast growth factor 23 requires O-glycosylation. J Biol Chem 281: 18370–18377, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

