Ontogenetic niche shifts as a driver of seasonal migration
- PMID: 32529317
- PMCID: PMC7320946
- DOI: 10.1007/s00442-020-04682-0
Ontogenetic niche shifts as a driver of seasonal migration
Abstract
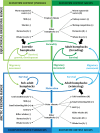
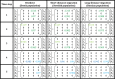
Ontogenetic niche shifts have helped to understand population dynamics. Here we show that ontogenetic niche shifts also offer an explanation, complementary to traditional concepts, as to why certain species show seasonal migration. We describe how demographic processes (survival, reproduction and migration) and associated ecological requirements of species may change with ontogenetic stage (juvenile, adult) and across the migratory range (breeding, non-breeding). We apply this concept to widely different species (dark-bellied brent geese (Branta b. bernicla), humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) and migratory Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) to check the generality of this hypothesis. Consistent with the idea that ontogenetic niche shifts are an important driver of seasonal migration, we find that growth and survival of juvenile life stages profit most from ecological conditions that are specific to breeding areas. We suggest that matrix population modelling techniques are promising to detect the importance of the ontogenetic niche shifts in maintaining migratory strategies. As a proof of concept, we applied a first analysis to resident, partial migratory and fully migratory populations of barnacle geese (Branta leucopsis). We argue that recognition of the costs and benefits of migration, and how these vary with life stages, is important to understand and conserve migration under global environmental change.
Keywords: Barnacle goose; Dark-bellied brent goose; Humpback whale; Matrix population modelling; Ontogeny; Pacific salmon; Reproduction; Seasonal migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alerstam T, Hedenström A, Åkesson S. Long-distance migration: evolution and determinants. Oikos. 2003;103:247–260.
-
- Alexandrou MA, Swartz BA, Matzke NJ, Oakley TH. Genome duplication and multiple evolutionary origins of complex migratory behavior in Salmonidae. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013;69:514–523. - PubMed
-
- Altizer S, Bartel R, Han BA. Animal migration and infectious disease risk. Science. 2011;331:296–302. - PubMed
-
- Avgar T, Street G, Fryxell JM. On the adaptive benefits of mammal migration. Can J Zool. 2014;92:481–490.
-
- Aydin KY, McFarlane GA, King JR, Megrey BA, Myers KW. Linking oceanic food webs to coastal production and growth rates of Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus spp.), using models on three scales. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr. 2005;52:757–780.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

