Decoding SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Evolution and Ramifications for COVID-19 Diagnosis, Vaccine, and Medicine
- PMID: 32530284
- PMCID: PMC7318555
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00501
Decoding SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Evolution and Ramifications for COVID-19 Diagnosis, Vaccine, and Medicine
Abstract
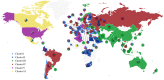
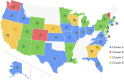
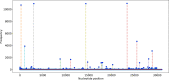
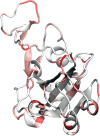
Tremendous effort has been given to the development of diagnostic tests, preventive vaccines, and therapeutic medicines for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Much of this development has been based on the reference genome collected on January 5, 2020. Based on the genotyping of 15 140 genome samples collected up to June 1, 2020, we report that SARS-CoV-2 has undergone 8309 single mutations which can be clustered into six subtypes. We introduce mutation ratio and mutation h-index to characterize the protein conservativeness and unveil that SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein, main protease, and endoribonuclease protein are relatively conservative, while SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, spike protein, and papain-like protease are relatively nonconservative. In particular, we have identified mutations on 40% of nucleotides in the nucleocapsid gene in the population level, signaling potential impacts on the ongoing development of COVID-19 diagnosis, vaccines, and antibody and small-molecular drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






References
-
- Cao Y.; Su B.; Guo X.; Sun W.; Deng Y.; Bao L.; Zhu Q.; Zhang X.; Zheng Y.; Geng C.; Chai X.; He R.; Li X.; Lv Q.; Zhu H.; Deng W.; Xu Y.; Wang Y.; Xie X. Potent neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 identified by high-throughput single-cell sequencing of convalescent patients b cells. Cell 2020, 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang C.; Michalska K.; Jedrzejczak R.; Maltseva N.; Endres M.; Godzik A.; Kim Y.; Joachimiak A.. Crystal structure of RNA binding domain of nucleocapsid phosphoprotein from SARS coronavirus 2. Wordwide PDB; 2020;10.2210/pdb6VYO/pdb. - DOI
-
- Corman V. M.; Landt O.; Kaiser M.; Molenkamp R.; Meijer A.; Chu D. K.; Bleicker T.; Brnink S.; Schneider J.; Schmidt M. L.; Mulders D. G.; Haagmans B. L.; van der Veer B.; van den Brink S.; Wijsman L.; Goderski G.; Romette J.-L.; Ellis J.; Zambon M.; Peiris M.; Goossens H.; Reusken C.; Koopmans M. P.; Drosten C. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-ncov) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeDiego M. L.; Nieto-Torres J. L.; Jiménez-Guardeño J. M.; Regla-Nava J. A.; Alvarez E.; Oliveros J. C.; Zhao J.; Fett C.; Perlman S.; Enjuanes L. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein regulates cell stress response and apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7 (10), e1002315.10.1371/journal.ppat.1002315. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ding C.; He X.. K-means clustering via principal component analysis. In Proceedings of the twenty-first international conference on Machine learning, 2004, p 29.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

