International Rare Cancers Initiative Multicenter Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Fluorouracil Versus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in Advanced Anal Cancer: InterAAct
- PMID: 32530769
- PMCID: PMC7406334
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.03266
International Rare Cancers Initiative Multicenter Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Fluorouracil Versus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in Advanced Anal Cancer: InterAAct
Abstract
Purpose: To compare cisplatin plus fluorouracil (FU) versus carboplatin plus paclitaxel in chemotherapy-naïve advanced anal cancer to establish the optimal regimen.
Patients and methods: Patients who had not received systemic therapy for advanced anal cancer were randomly assigned 1:1 to intravenous cisplatin 60 mg/m2 (day 1) plus FU 1,000 mg/m2 (days 1-4) every 21 days or carboplatin (area under the curve, 5; day 1) plus paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 (days 1, 8, and 15) every 28 days for 24 weeks, until disease progression, intolerable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent. Primary end point was objective response rate (ORR). Primary and secondary end points were assessed in a hierarchic model to compare the regimens and pick the winner.
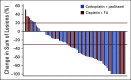
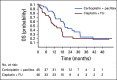
Results: We conducted an international multicenter randomized phase II study in 60 centers between December 2013 and November 2017. Median follow-up was 28.6 months. A total of 91 patients were randomly assigned: 46 to cisplatin plus FU and 45 to carboplatin plus paclitaxel. ORR was 57% (95% CI, 39.4% to 73.7%) for cisplatin plus FU versus 59% (95% CI, 42.1% to 74.4%) for carboplatin plus paclitaxel. More serious adverse events were noted in the cisplatin plus FU arm (62%) compared with the carboplatin plus paclitaxel arm (36%; P = .016). Median progression-free survival was 5.7 months (95% CI, 3.3 to 9.0 months) for cisplatin plus FU compared with 8.1 months (95% CI, 6.6 to 8.8 months) for carboplatin plus paclitaxel. Median overall survival was 12.3 months for cisplatin plus FU (95% CI, 9.2 to 17.7 months) compared with 20 months (95% CI, 12.7 months to not reached) for carboplatin plus paclitaxel (hazard ratio, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.15 to 3.47; P = .014).
Conclusion: This is the first international randomized trial to our knowledge conducted in chemotherapy-naïve advanced anal cancer. Although there was no difference in ORR, the association with clinically relevant reduced toxicity and a trend toward longer survival suggest that carboplatin plus paclitaxel should be considered as a new standard of care.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02051868.
Figures
Comment in
-
How to Choose the Right Treatment for Patients With Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Absence of a Comparative Randomized Clinical Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Nov 20;38(33):3973-3974. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02137. Epub 2020 Oct 7. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33026940 No abstract available.
-
Reply to S. Kim et al.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Nov 20;38(33):3974-3975. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02643. Epub 2020 Oct 7. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33026941 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nelson VM, Benson AB., III Epidemiology of anal canal cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2017;26:9–15. - PubMed
-
- van der Zee RP, Richel O, de Vries HJ, et al. The increasing incidence of anal cancer: Can it be explained by trends in risk groups? Neth J Med. 2013;71:401–411. - PubMed
-
- Islami F, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, et al. International trends in anal cancer incidence rates. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46:924–938. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. https://seer.cancer.gov/