Rapid detection of novel coronavirus/Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification
- PMID: 32530929
- PMCID: PMC7292379
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234682
Rapid detection of novel coronavirus/Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Abstract
Novel Corona virus/Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or 2019-nCoV), and the subsequent disease caused by the virus (coronavirus disease 2019 or COVID-19), is an emerging global health concern that requires a rapid diagnostic test. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) is currently the standard for SARS-CoV-2 detection; however, Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) may allow for faster and cheaper field based testing at point-of-risk. The objective of this study was to develop a rapid screening diagnostic test that could be completed in 30-45 minutes. Simulated patient samples were generated by spiking serum, urine, saliva, oropharyngeal swabs, and nasopharyngeal swabs with a portion of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleic sequence. RNA isolated from nasopharyngeal swabs collected from actual COVID-19 patients was also tested. The samples were tested using RT-LAMP as well as by conventional qRT-PCR. Specificity of the RT-LAMP was evaluated by also testing against other related coronaviruses. RT-LAMP specifically detected SARS-CoV-2 in both simulated patient samples and clinical specimens. This test was performed in 30-45 minutes. This approach could be used for monitoring of exposed individuals or potentially aid with screening efforts in the field and potential ports of entry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

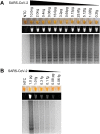
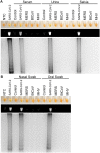
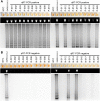
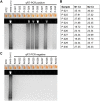
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

