Validity, reliability and cut-offs of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 as a screening tool for depression among patients living with epilepsy in Rwanda
- PMID: 32530968
- PMCID: PMC7292570
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234095
Validity, reliability and cut-offs of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 as a screening tool for depression among patients living with epilepsy in Rwanda
Abstract
Background: Patients with epilepsy (PwE) have an increased risk of active and lifetime depression. Two in 10 patients experience depression. Lack of trained psychiatric staff in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC) creates a need for screening tools that enable detection of depression in PwE. We describe the translation, validity and reliability assessment of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) as a screening tool for depression among PwE in Rwanda.
Method: PHQ-9 was translated to Kinyarwanda using translation-back translation and validated by a discussion group. For validation, PwE of ≥15 years of age were administered the PHQ-9 and Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) by trained psychiatry staff at Visit 1. A random sample of 20% repeated PHQ-9 and HDRS after 14 days to assess temporal stability and intra-rater reliability. Internal structure, reliability and external validity were assessed using confirmatory factor analysis, reliability coefficients and HDRS-correlation, respectively. Maximal Youden's index was considered for cut-offs.
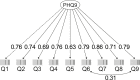
Results: Four hundred and thirty-four PwE, mean age 30.5 years (SD ±13.3), were included of whom 33.6%, 37.9%, 13.4%, and 15.1% had no, mild, moderate and severe depression, respectively. PHQ-9 performed well on a one-factor model (unidimensional model), with factor loadings of 0.63-0.86. Reliability coefficients above 0.80 indicated strong internal consistency. Good temporal stability was observed (0.79 [95% CI: 0.68-0.87]). A strong correlation (R = 0.66, p = 0.01) between PHQ-9 and HDRS summed scores demonstrated robust external validity. The optimal cut-off for the PHQ-9 was similar (≥5) for mild and moderate depression and ≥7 for severe depression.
Conclusion: PHQ-9 validation in Kinyarwanda creates the capacity to screen PwE in Rwanda at scores of ≥5 for mild or moderate and ≥7 for severe depression. The availability of validated tools for screening and diagnosis for depression is a forward step for holistic care in a resource-limited environment.
Conflict of interest statement
PD has received consultancy fees from UCB Pharma and Novartis. DET is an employee of UCB Pharma. PEB has received speaker and consultancy fees from UCB Pharma and grants from his institution. JNRV received a consultancy fee for the statistical analysis. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. Other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures